-

-
Dynamic Shear Behavior Characteristics of PHC Pile-cohesive Soil Ground Contact Interface Considering Various Environmental Factors
다양한 환경인자를 고려한 PHC 말뚝-사질토 지반 접촉면의 동적 전단거동 특성
-
Young-Jun Kim, Chang-Won Kwak, Inn-Joon Park
김영준, 곽창원, 박인준
- PHC piles demonstrate superior resistance to compression and bending moments, and their factory-based production enhances quality assurance and management processes. Despite these …
PHC 말뚝은 압축력 및 휨 모멘트에 대한 저항력이 우수하며, 공장에서의 생산으로 인해 품질 관리가 효율적으로 이루어진다. 이러한 장점으로 인해 다양한 토목 및 …
- PHC piles demonstrate superior resistance to compression and bending moments, and their factory-based production enhances quality assurance and management processes. Despite these advantages that have resulted in widespread use in civil engineering and construction projects, the design process frequently relies on empirical formulas or N-values to estimate the soil-pile friction, which is crucial for bearing capacity, and this reliance underscores a significant lack of experimental validation. In addition, environmental factors, e.g., the pH levels in groundwater and the effects of seawater, are commonly not considered. Thus, this study investigates the influence of vibrating machine foundations on PHC pile models in consideration of the effects of varying pH conditions. Concrete model piles were subjected to a one-month conditioning period in different pH environments (acidic, neutral, and alkaline) and under the influence of seawater. Subsequent repeated direct shear tests were performed on the pile-soil interface, and the disturbed state concept was employed to derive parameters that effectively quantify the dynamic behavior of this interface. The results revealed a descending order of shear stress in neutral, acidic, and alkaline conditions, with the pH-influenced samples exhibiting a more pronounced reduction in shear stress than those affected by seawater.
- COLLAPSE
PHC 말뚝은 압축력 및 휨 모멘트에 대한 저항력이 우수하며, 공장에서의 생산으로 인해 품질 관리가 효율적으로 이루어진다. 이러한 장점으로 인해 다양한 토목 및 건축 현장에서 널리 활용되고 있지만, PHC 말뚝의 설계 과정에서 중요한 요소인 주면 마찰력은 주로 경험식이나 N 값 등의 추정치를 기반으로 하고 있다. 이에 대한 실험적 연구는 상대적으로 부족하며, 환경적 요소 중 하나인 pH 값과 지하수 또는 해수의 영향 역시 간과되는 경우가 많다. 본 연구에서는 진동기계 기초의 영향을 받는 PHC 말뚝 모델을 중심으로 다양한 pH 환경(산성, 중성, 염기성) 및 해수의 영향 하에 한 달 동안 수침 후, 해당 PHC 말뚝-사질토의 접촉면에 대한 반복 단순 전단시험을 수행하였다. 이를 위해 교란 상태 개념(Disturbed State Concept)을 적용하여 접촉면의 동적 거동을 정량적으로 평가하였다. 연구 결과, 화학적 환경에 따른 동적 전단응력은 중성 > 산성 > 염기성 순으로 감소하였다. 또한, pH 영향을 받은 경우와 해수의 영향을 받은 경우를 비교했을 때, pH 영향을 받은 경우에 전단응력의 감소가 더 크게 나타났다.
-
Dynamic Shear Behavior Characteristics of PHC Pile-cohesive Soil Ground Contact Interface Considering Various Environmental Factors
-
-
Image-Data-Acquisition and Data-Structuring Methods for Tunnel Structure Safety Inspection
터널 구조물 안전점검을 위한 이미지 데이터 취득 및 데이터 구조화 방법
-
Hyun-Suk Sung, Joon-Sub Koh
성현석, 고준섭
- This paper proposes a method to acquire image data inside tunnel structures and a method to structure the acquired image data. By …
본 연구에서는 터널 구조물 내부 이미지 데이터를 취득하는 방법과 이미지 데이터의 구조화를 위한 방법을 제안하였다. 터널 구조물 내부 이미지 데이터 취득 조건을 …
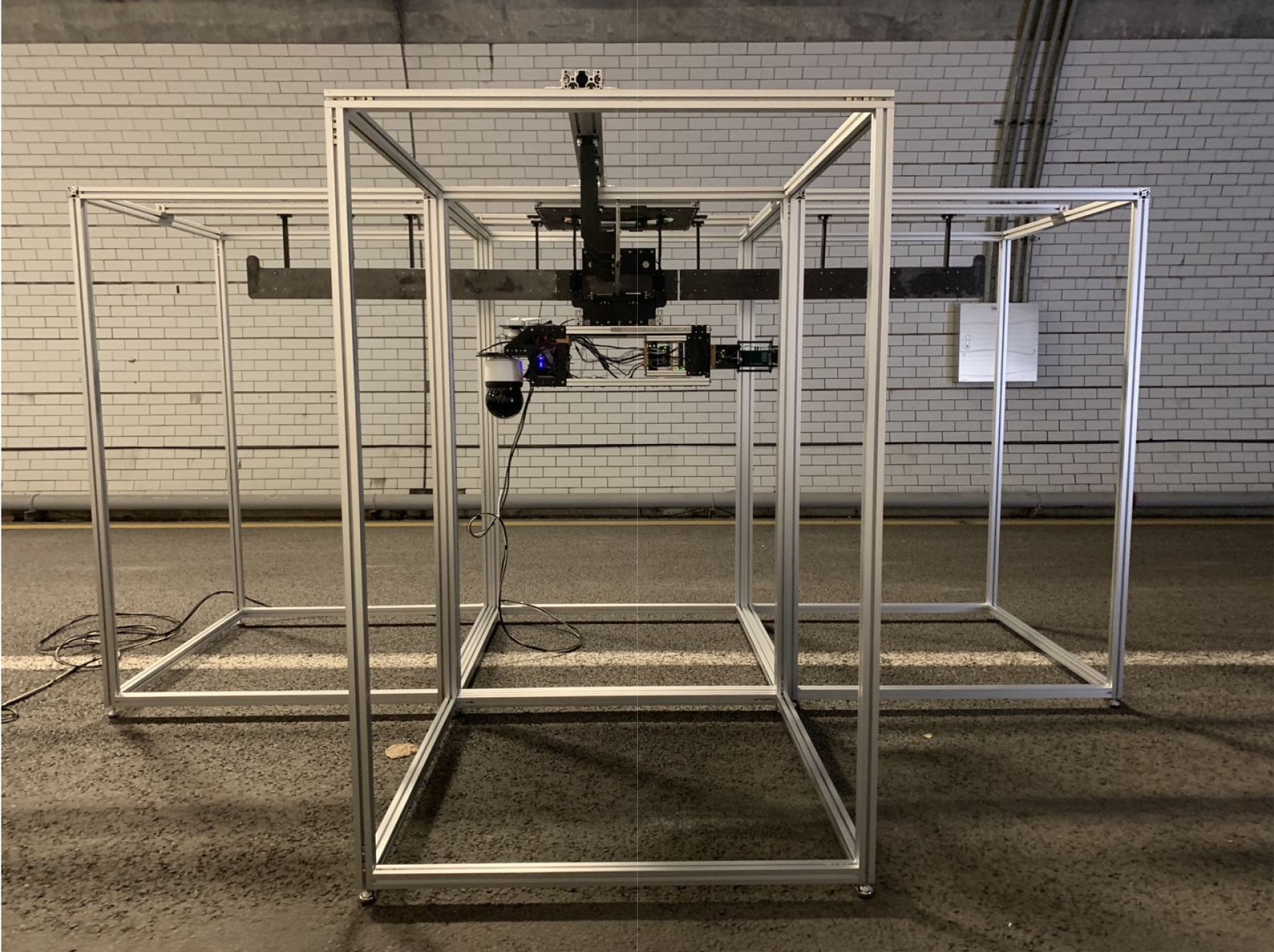
- This paper proposes a method to acquire image data inside tunnel structures and a method to structure the acquired image data. By improving the conditions by which image data are acquired inside the tunnel structure, high-quality image data can be obtained from area type tunnel scanning. To improve the data acquisition conditions, a longitudinal rail of the tunnel can be installed on the tunnel ceiling, and image data of the entire tunnel structure can be acquired by moving the installed rail. This study identified 0.5 mm cracked simulation lines under a distance condition of 20 m at resolutions of 3,840 × 2,160 and 720 × 480 pixels. In addition, the proposed image-data-structuring method could acquire image data in image tile units. Here, the image data of the tunnel can be structured by substituting the application factors (resolution of the acquired image and the tunnel size) into a relationship equation. In an experiment, the image data of a tunnel with a length of 1,000 m and a width of 20 m were obtained with a minimum overlap rate of 0.02% to 8.36% depending on resolution and precision, and the size of the local coordinate system was found to be (14 × 15) to (36 × 34) pixels.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 터널 구조물 내부 이미지 데이터를 취득하는 방법과 이미지 데이터의 구조화를 위한 방법을 제안하였다. 터널 구조물 내부 이미지 데이터 취득 조건을 개선함으로써 AREA TYPE의 터널 스캐닝에서 고화질의 이미지 데이터를 얻을 수 있다. 데이터 취득 조건을 개선하기 위해 터널 상부에 터널의 길이 방향 레일을 설치하고 설치된 레일을 이동하며 터널 구조물 전체의 이미지 데이터를 취득할 수 있도록 설계하였다. 본 연구는 거리 20m, 해상도 3840×2160 및 해상도 720×480의 조건에서 0.5mm 균열 모사선을 식별하였다. 또한 취득된 이미지 데이터를 이미지 타일 단위로 관리하기 위한 이미지 데이터 구조화 방법을 제안하였다. 터널의 이미지 데이터 구조화를 위해 적용인자(취득 이미지의 해상도와 터널의 크기)를 관계식에 대입하여 터널의 이미지 데이터를 구조화할 수 있다. 실험을 통해 터널 길이 1,000m, 폭 20m 터널의 이미지 데이터는 해상도와 정밀도에 따라 최소중첩률 0.02%에서 8.36% 구해지며 로컬좌표계의 크기는 (14×15)에서 (36×34)로 나타났다.
-
Image-Data-Acquisition and Data-Structuring Methods for Tunnel Structure Safety Inspection
-

-
Quality Enhancement of Recycled Concrete Aggregates for Backfill Materials by CO2 Carbonation: Development of a 5-kg-scale Prototype Reactor
이산화탄소의 탄산화 반응을 이용한 되메움재용 순환골재의 품질 개량: 5kg급 프로토타입 반응조 개발
-
Jinwoo Kim, Min-Kyung Jeon, Tae-Hyuk Kwon, Nam-Ryong Kim
김진우, 전민경, 권태혁, 김남룡
- In this study, recycled concrete aggregates (RCA) were treated in a 5-kg-scale prototype reactor with carbon dioxide (CO2) to enhance …
본 연구에서는 이산화탄소 처리를 통한 순환골재의 지반공학적 성능 개량을 평가하기 위하여 5kg급 프로토타입 반응조를 제작하였다. 제작된 반응조를 이용하여 이산화탄소 처리한 순환골재와 미처리 …
- In this study, recycled concrete aggregates (RCA) were treated in a 5-kg-scale prototype reactor with carbon dioxide (CO2) to enhance their material quality and geotechnical performance. The aggregate crushing value (ACV) and California bearing ratio (CBR) were measured on untreated RCAs and CO2-treated RCAs. After CO2 treatment, the ACV decreased from 35.6% to 33.2%, and the CBR increased from 97.5% to 102.4%. The CO2 treatment caused a reduction of fine particle generation and an increase in bearing capacity through carbonation. When CO2 treatment was performed with mechanical agitation, which provided additional enhancement in mechanical quality, the ACV was reduced further to 30.3%, and the CBR increased to 137.7%. If upscaled effectively, the proposed CO2 treatment technique would be an effective method to reduce carbon emissions in construction industries.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 이산화탄소 처리를 통한 순환골재의 지반공학적 성능 개량을 평가하기 위하여 5kg급 프로토타입 반응조를 제작하였다. 제작된 반응조를 이용하여 이산화탄소 처리한 순환골재와 미처리 순환골재의 골재 파쇄값과 노상토지지력비를 측정하였다. 이산화탄소 처리를 통해 골재 파쇄값은 35.6%에서 33.2%로 2.4% 감소하고 노상토지지력비는 97.5%에서 102.4%로 4.9% 증가하는 것이 관찰되었다. 탄산화 반응을 통해 생성된 탄산칼슘 염으로 인해 순환골재의 세립분 생성이 감소하고 지지력이 증가함을 알 수 있었다. 또한 교반을 함께할 경우 추가적인 역학적 개량 효과를 통해 골재 파쇄값이 30.3%로 감소하고 노상토지지력비는 137.7%로 증가하였다. 본 연구에서 기술된 이산화탄소 처리 기술의 현장 적용 시 건설 산업의 탄소배출을 효과적으로 줄일 수 있을 것으로 보인다.
-
Quality Enhancement of Recycled Concrete Aggregates for Backfill Materials by CO2 Carbonation: Development of a 5-kg-scale Prototype Reactor
-
-
Preliminary Study on Alluvial Soil Characteristics for Clogging Possibility in Groundwater Artificial Recharge Area
인공함양 지역 클로깅 가능성 평가를 위한 충적층 토양 특성에 관한 예비 연구
-
Jeong Hwang, Myoung-Rak Choi, Gyoo-Bum Kim
황정, 최명락, 김규범
- Artificial recharge systems have been employed to solve drought problems due to global climate change. Despite the increased usage, the applications of …
전 지구적 기후변화에 따른 용수확보 방안으로 인공함양 기법이 활용되고 있다. 함양률을 감소시키는 클로깅 문제는 인공함양 기법의 활용에 큰 장애가 되고 있다. 이 …
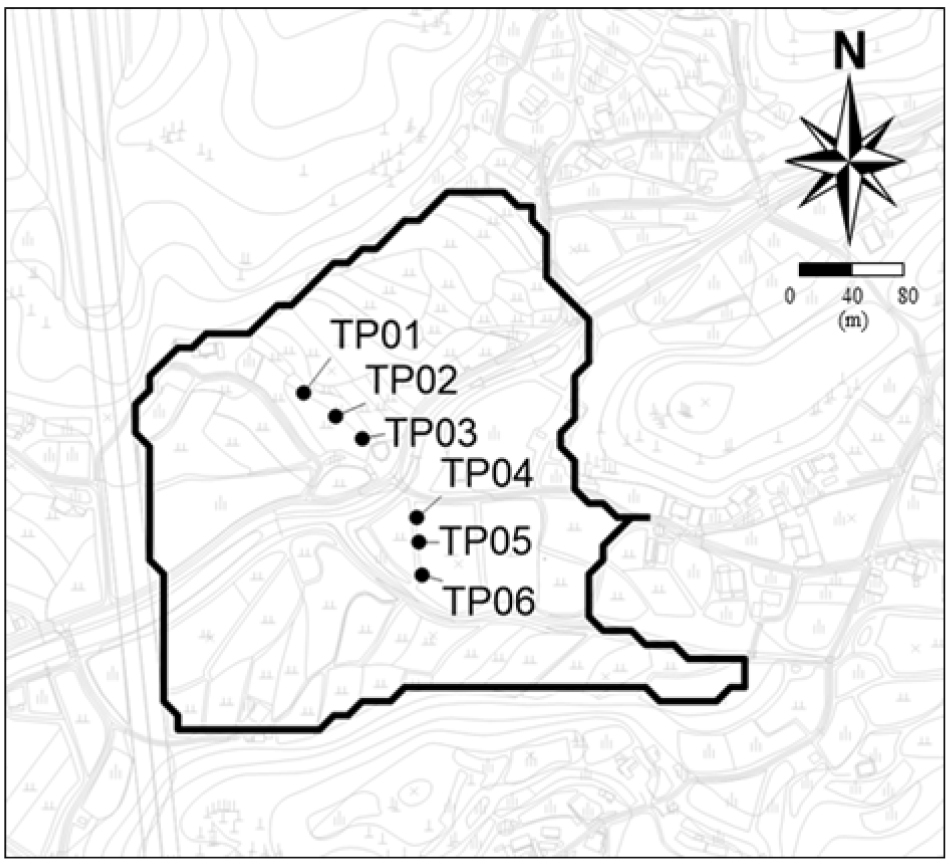
- Artificial recharge systems have been employed to solve drought problems due to global climate change. Despite the increased usage, the applications of artificial recharge systems are limited by clogging problems, which reduce recharge rates. In this study, the soil texture and mineral characteristics of alluvial soil in a planned artificial recharge system area were investigated to evaluate the possibility of chemical clogging during the injection of stream water. The primary minerals contained in the clastic particles are quartz, K-feldspar, plagioclase, and biotite, and the secondary minerals filling the pore space are illite, kaolinite and Fe-oxide. The fact that carbonate and sulfate are observed as secondary minerals in the pore space suggests that chemical clogging has not occurred by the interaction between the groundwater and surface water in the study area. Thus, monitoring soil properties, e.g., the formation and growth of secondary minerals in the pore space, is required to investigate the possibility of chemical clogging in artificial recharge systems.
- COLLAPSE
전 지구적 기후변화에 따른 용수확보 방안으로 인공함양 기법이 활용되고 있다. 함양률을 감소시키는 클로깅 문제는 인공함양 기법의 활용에 큰 장애가 되고 있다. 이 연구는 하천수 주입 과정에서 발생할 가능성이 있는 클로깅 평가를 위한 기초자료를 확보하기 위해 인공함양 예정 지역 충적층의 토양 조직과 광물 특성을 분석하였다. 충적층 쇄설성 입자의 주요 구성 광물은 석영, 정장석, 사장석, 흑운모 등이며, 공극을 충진하는 주요 2차 광물은 일라이트, 카오린나이트, Fe-산화광물이다. 2차 광물로서 탄산염 혹은 황산염 광물의 산출이 없는 것은 인공함양 실험 전인 연구지역 충적층에서는 지하수와 지표수 간의 반응에 의한 화학적 클로깅은 발생하지 않았음을 시사한다. 인공함양 실험과 관련된 화학적 클로깅에 대한 평가를 위해 대수층 내 공극에서 2차 광물의 생성과 성장과 같은 충적층의 토양 특성에 대한 모니터링이 필요하다.
-
Preliminary Study on Alluvial Soil Characteristics for Clogging Possibility in Groundwater Artificial Recharge Area
-
-
Soil-Water Characteristic Curves for Drying and Wetting Processes in Granite-Weathered Soil Based on Variations in Fine Contents
세립분 함량을 고려한 국내 화강풍화토의 건조 및 습윤 함수특성곡선 분석
-
Sangbeen Lee, Jae-Eun Ryou, Jinuk Seo, Jongwon Jung
이상빈, 유재은, 서진욱, 정종원
- In current slope stability analysis techniques, slope stability is evaluated based on the saturated-soil theory. However, soil-water characteristics change frequently depending on …
기존의 사면안정해석은 포화토 이론에 기반하여 비탈면 안정성에 대한 평가가 진행되었다. 그러나 자연 지반은 기후에 따라 함수 특성이 변화하기 때문에 포화토 이론은 한계가 …
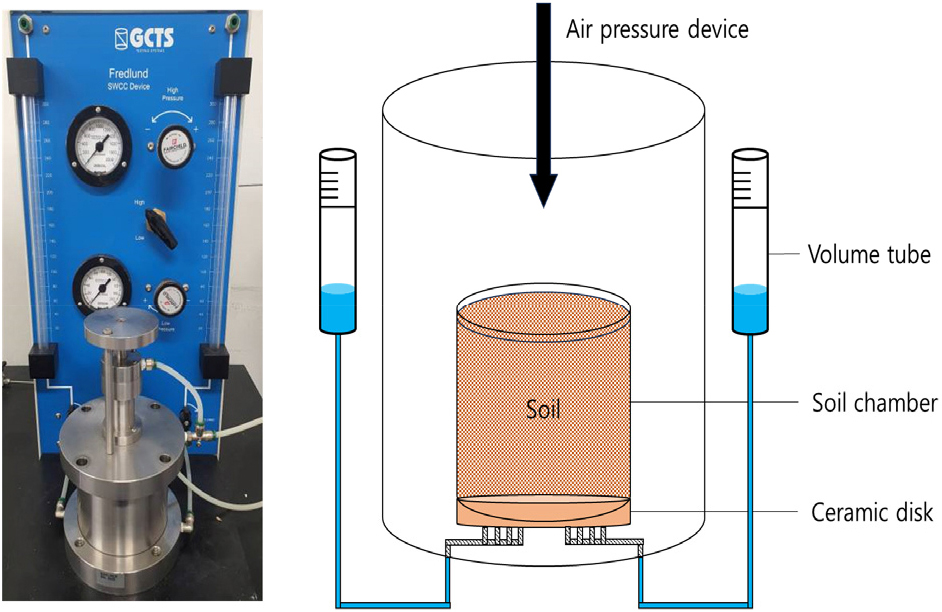
- In current slope stability analysis techniques, slope stability is evaluated based on the saturated-soil theory. However, soil-water characteristics change frequently depending on the climate. Therefore, because the saturated soil theory has limitations, the application of the unsaturated soil theory is necessary for slope stability. It is also important to evaluate the engineering properties of unsaturated soil because the capillary absorption capacity is reduced due to heavy rain, thereby causing a reduction in slope stability. In this study, soil-water characteristic tests were performed using four samples with different fine contents (0%, 10%, 20%, and 30%) using granite-weathered soil in domestic production areas. In particular, to consider the previously conducted drying process as well as the evaluation of stability due to heavy rain on the actual slope, a wetting process was conducted, in which the water content was increased. In addition, the van Genuchten (1980) model, which is the most consistent theoretical equation for the experiment, was used with various theoretical equations, and the parameters were analyzed according to the fine content of the granite-weathered soil for the drying and wetting processes.
- COLLAPSE
기존의 사면안정해석은 포화토 이론에 기반하여 비탈면 안정성에 대한 평가가 진행되었다. 그러나 자연 지반은 기후에 따라 함수 특성이 변화하기 때문에 포화토 이론은 한계가 있어 불포화토의 특성을 고려한 안정해석 연구가 필요하다. 또한, 실제 불포화토 지반은 호우로 인해 모관흡수력이 감소하여 사면 안정성의 저감을 유발하기 때문에 이에 대한 공학적 특성을 평가하는 것이 중요한 실정이다. 본 연구에서는 국내 산지에 내포된 화강풍화토를 활용하여 세립분 함량을 0%, 10%, 20%, 30%로 구분한 4가지 시료를 통해 흙-함수 특성 시험을 수행하였으며, 특히 건조과정 뿐만 아니라 실제 사면에서 호우로 인한 안정성 평가를 고려하기 위해 함수비를 증가시키는 습윤과정을 진행하였다. 또한, 다양한 이론식을 적용하여 실험에 가장 일치하는 이론식인 van Genuchten(1980) 모델을 활용하였으며, 건조과정과 습윤과정에 대한 화강풍화토의 세립분에 따른 파라미터를 분석하였다.
-
Soil-Water Characteristic Curves for Drying and Wetting Processes in Granite-Weathered Soil Based on Variations in Fine Contents
-
-
Development of Thermomechanical Coupled Numerical Model for Energy Slab
에너지 슬래브의 열-역학적 수치해석 모델 개발
-
Sangwoo Park, Hangseok Choi, Seokjae Lee
박상우, 최항석, 이석재
- In this study, a thermomechanical numerical model was developed to evaluate the stability of energy slabs. First, a wall-type energy slab was …
본 연구에서는 에너지 슬래브의 안정성을 검토하기 위해 열-역학적 수치해석 모델을 개발하였다. 먼저, 주거용 건물 지하주차장에 벽체형 에너지 슬래브를 설치한 뒤 현장 열성능 …
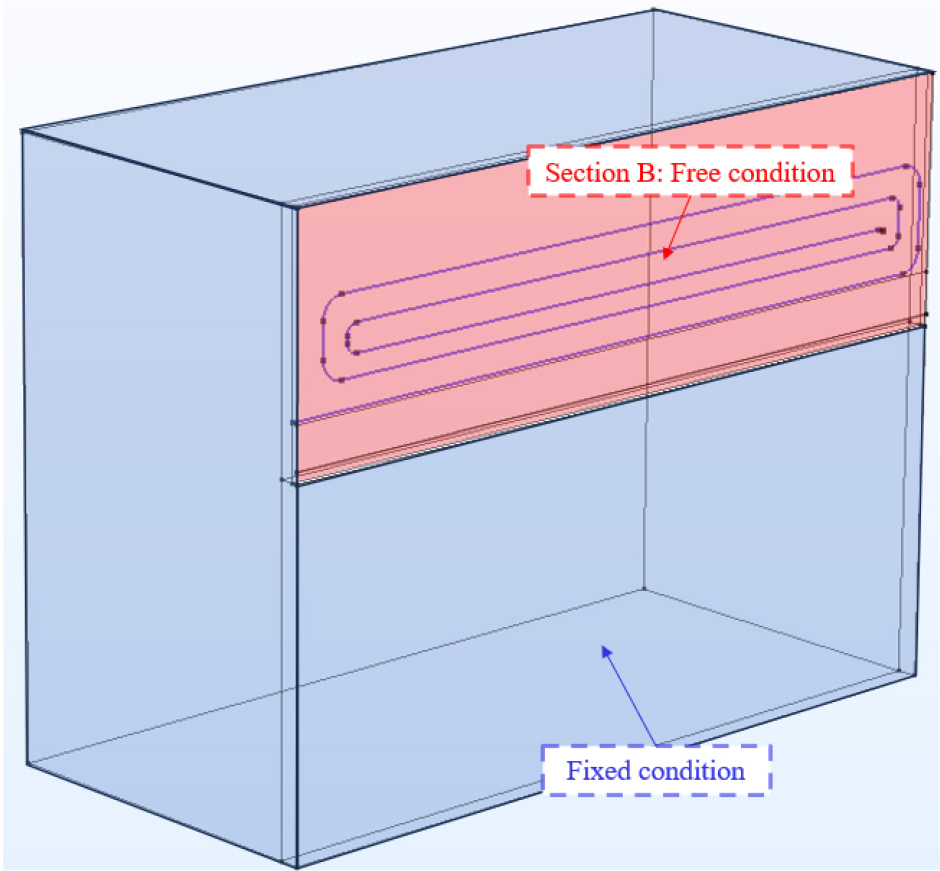
- In this study, a thermomechanical numerical model was developed to evaluate the stability of energy slabs. First, a wall-type energy slab was installed in a residential underground parking lot, and thermal performance tests were conducted. Based on the tests, a numerical thermohydraulics model of the energy slab was developed to accurately simulate the thermal behavior in thermal performance tests. Finally, utilizing the temperature data acquired using the developed model, a thermomechanical numerical model of the energy slab was established. The thermomechanical model was then used to simulate the thermal stresses induced by operating the energy slab. The results demonstrated a maximum thermal stress of 5,300 kPa, which highlights the need to utilize cement mortar with sufficient tensile strength to realize stable operation of the energy slab.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 에너지 슬래브의 안정성을 검토하기 위해 열-역학적 수치해석 모델을 개발하였다. 먼저, 주거용 건물 지하주차장에 벽체형 에너지 슬래브를 설치한 뒤 현장 열성능 평가시험(Thermal performance test, TPT)을 수행하였다. 이를 기반으로 현장 열성능 평가시험의 열-수리학적 거동을 정교하게 모사할 수 있는 에너지 슬래브의 열-수리학적 수치해석 모델을 개발하였다. 마지막으로, 열-수리학적 모델을 통해 도출된 시간-온도 데이터를 기반으로 에너지 슬래브의 열-역학적 수치해석 모델을 개발하였다. 개발된 모델을 기반으로 에너지 슬래브의 운용에 따른 열응력을 산정한 결과 최대 5,300kPa의 열응력이 발생하였으며, 이는 에너지 슬래브의 안정적인 운용을 위해 충분한 인장강도가 확보된 시멘트 몰탈 활용이 필요하다는 것을 시사한다.
-
Development of Thermomechanical Coupled Numerical Model for Energy Slab
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society











