-
-
Effect of PVA on Increasing Strength of Steel-Slag-Treated Clay and Applicability to Port and Harbor Improvement
PVA를 혼합한 제강슬래그의 강도증가 경향 및 항만개선에 대한 적용성 조사
-
Odate Yuya, Hata Toshiro, Won-jin Beak, Chiwoon Jang, Jihoon Jeong, Yunha Joo
오다테유야, 하타토시로, 백원진, 장치운, 정지훈, 주윤하
- Recently, the use of soil mixed with steelmaking slag (hereafter steelmaking slag‒mixed soil) as a landfill material for port construction projects has …
최근, 항만공사를 위한 매립재로 제강슬래그 혼합토의 사용이 증가하고 있는 실정이다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 제강슬래그 혼합토의 초기강도증진과 해양투기시의 탁도제어 및 양생기간의 단축을 목적으로 …
- Recently, the use of soil mixed with steelmaking slag (hereafter steelmaking slag‒mixed soil) as a landfill material for port construction projects has been increasing. Through laboratory tests, the effects of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), a synthetic resin, on enhancing the initial strength and applicability of steelmaking slag-mixed soil, controlling turbidity during ocean dumping, and shortening the curing periods were examined. Vane shear tests and unconfined compression tests were conducted with varying amounts of slag and PVA to determine the optimal mix. The void ratio was calculated and the factors contributing to the observed change in strength were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy. Finally, to evaluate the applicability for port construction, turbidity and seawater exposure tests were conducted to assess the potential for the practical application of steel-slag-treated clay with PVA. Uniaxial compression tests of the samples cured for different periods showed that the use of PVA increased the initial strength owing to its adhesive properties, but the strength tended to decrease as curing progressed owing to an increase in the number of voids within the specimen and inhibition of the hydration reaction. Moreover, the combination with PVA did not lead to negative effects upon exposure to seawater. The effect on turbidity control immediately after curing of the mixed soil and the long-term durability in a seawater environment were also confirmed, indicating that the composite can be applied in port maintenance.
- COLLAPSE
최근, 항만공사를 위한 매립재로 제강슬래그 혼합토의 사용이 증가하고 있는 실정이다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 제강슬래그 혼합토의 초기강도증진과 해양투기시의 탁도제어 및 양생기간의 단축을 목적으로 합성수지인 PVA를 병용했을 때의 강도증진경향 및 항만정비시의 적용성을 실내실험을 통해 검토하였다. 본 연구에서는 슬래그와 PVA의 함량을 달리하여 베인 전단 시험과 일축 압축 시험을 수행하여 최적의 배합을 결정하였다. 다음으로, 공극률을 계산하고, SEM 분석을 통해 강도 변화에 기여하는 요인을 분석하였다. 마지막으로, 항만 건설에 대한 적용 가능성을 평가하기 위해 탁도 시험과 해수 노출 시험을 수행하여 PVA로 처리된 철강 슬래그 점토의 실제 적용 가능성을 평가하였다. 양생기간을 달리한 일축압축시험결과, PVA를 사용하면 접착 특성으로 인해 초기 강도가 증가했지만, 시편 내 공극 증가와 수화 반응 억제로 인해 경화가 진행됨에 따라 강도가 시간이 지남에 따라 감소하는 경향이 나타났다. 또한, PVA를 병용사용함으로써 해수노출시의 부정적인 요소는 보이지 않았으며, 혼합토의 양생직후 탁도제어효과와 해수 환경하에서 장기적인 내구성이 확인되어 항만 정비시의 적용이 가능한 것으로 나타났다.
-
Effect of PVA on Increasing Strength of Steel-Slag-Treated Clay and Applicability to Port and Harbor Improvement
-
-
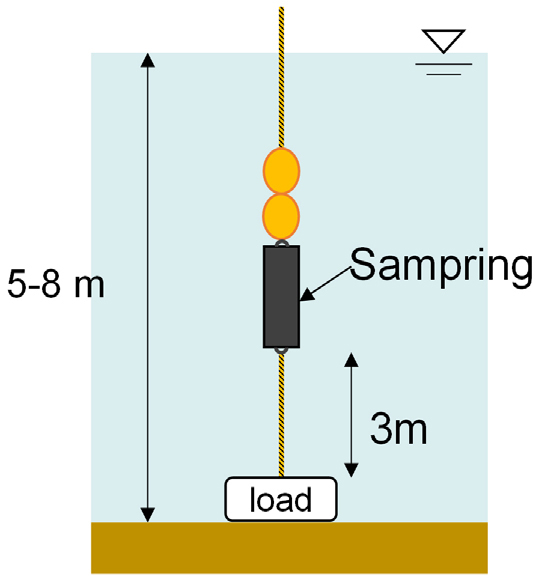
Stability of Soundproof Wall Foundations and the Reinforcement Effect of Micropiles
방음벽 기초의 안정성 및 마이크로파일 보강효과
-
Sung-Wook Choi, Young-Min Kim, Kang-Il Lee
최성욱, 김영민, 이강일
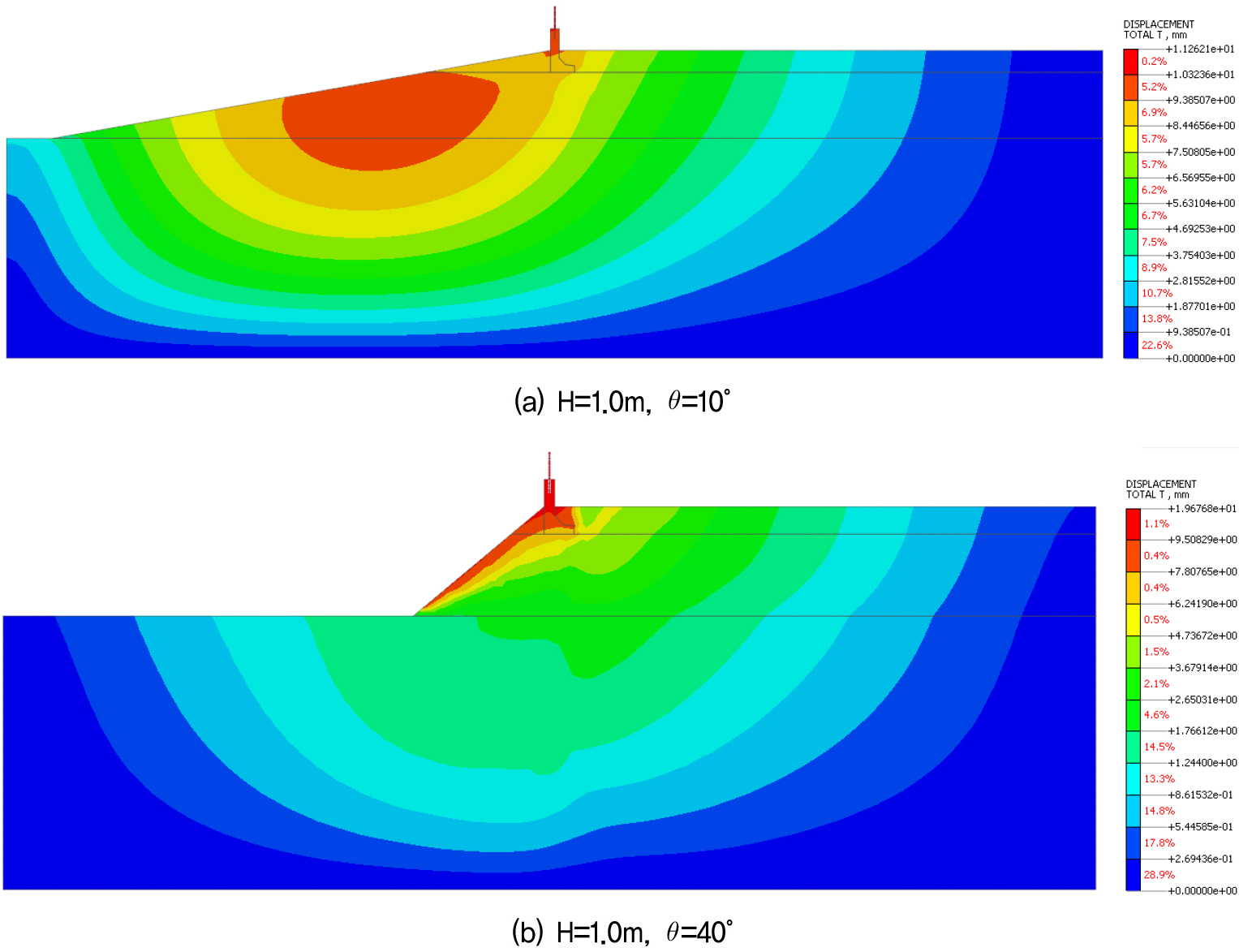
- This study numerically examines the stability of soundproof wall foundations on sloped ground and evaluates the reinforcement effect of micropiles in situations …
본 연구는 방음벽 기초가 설치되는 사면의 앞굽 경사에 따른 기초의 안정성을 수치해석을 통해 분석하고, 안정성이 확보되지 않는 조건에서 마이크로파일의 보강 효과를 정량적으로 …
- This study numerically examines the stability of soundproof wall foundations on sloped ground and evaluates the reinforcement effect of micropiles in situations where stability is compromised. Analysis using the strength reduction method revealed that front slopes steeper than 1:1.5 (approximately 33.3°) jeopardize foundation stability. The effectiveness of micropile reinforcement was assessed in terms of reductions in settlement and lateral displacement relative to pile length (L). The results indicated that significant displacement reduction occurred when the ratio of pile length to diameter (L/D) ≤ 30, with an optimal reinforcement range identified as 15 ≤ L/D ≤ 30, taking economic efficiency into account.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 방음벽 기초가 설치되는 사면의 앞굽 경사에 따른 기초의 안정성을 수치해석을 통해 분석하고, 안정성이 확보되지 않는 조건에서 마이크로파일의 보강 효과를 정량적으로 평가하였다. 강도감소법을 이용한 사면안정 해석 결과, 앞굽 경사가 1:1.5(약 33.3°)를 초과할 경우 기초 안정성이 확보되지 않았으며, 이에 마이크로파일을 설치하여 파일 설치 길이(L)에 따른 기초의 침하 및 수평변위 저감 효과를 분석하였다. 그 결과, 파일 설치 길이에 따른 변위 감소율은 L/D ≤ 30 범위 내에서 뚜렷하게 나타났으며, 경제적 측면을 고려할 때 15 ≤ L/D ≤ 30이 적정한 보강 길이로 판단된다.
-
Stability of Soundproof Wall Foundations and the Reinforcement Effect of Micropiles
-
-
Physics-inspired and Data-driven Analyses of Fluid Flow in Seafloor Sediments
물리적 모델과 데이터에 기반한 해저지반 투수계수 예측
-
Chaewon Park, Junghee Park
박채원, 박정희
- Climate change has led to a growing interest in seafloor geotechnical structures. Accurate prediction and assessment of the engineering properties of seafloor …
기후 변화로 인한 해수면 상승으로 인해 해저 에너지 지반 구조물에 대한 개발이 많은 관심을 받고 있다. 해저 지반의 공학적 물성치를 정확히 예측하고 …
- Climate change has led to a growing interest in seafloor geotechnical structures. Accurate prediction and assessment of the engineering properties of seafloor sediments provide reliable design parameters, which are essential for successful seafloor projects. In this study, we examine the critical role of diatoms in fluid flow within granular mixtures and propose a simplified analytical model based on experimental data for predicting hydraulic conductivity in seafloor sediments. We first prepare sand-diatom mixtures with varying diatom weight fractions and then conduct hydraulic conductivity tests. A comparison of the model and experimental results reveal three characteristic patterns of hydraulic conductivity as diatom content increases: (i) a sharp decrease due to diatom-filled pore spaces between sand grains, (ii) a transitional fluid flow with diatom-dominant pores, and (iii) a further reduction in hydraulic conductivity resulting from diatom-induced drag forces. This study highlights the effects of diatoms on fluid flow in seafloor sediments and demonstrates that a simple yet robust theoretical framework can effectively predict hydraulic conductivity in these sediments.
- COLLAPSE
기후 변화로 인한 해수면 상승으로 인해 해저 에너지 지반 구조물에 대한 개발이 많은 관심을 받고 있다. 해저 지반의 공학적 물성치를 정확히 예측하고 평가하는 것은 신뢰할 수 있는 설계 정수를 제공하며, 성공적인 해저지반 구조물 프로젝트에 기여할 수 있다. 본 연구에서는 해저지반에 널리 분포하며 일반적인 흙보다 훨씬 낮은 비중을 가지는 다이아톰을 포함한 지반 조건이 유체의 흐름에 미치는 영향을 데이터에 기반한 물리적 모델과 실내실험을 통해 파악하고자 하였다. 첫번째로, 다이아톰 슬러리의 점성을 고려한 입자의 삼상관계 분석을 통해 유체의 흐름을 결정하는 다이아톰 함량 예측을 이론적으로 접근하였다. 두번째로, 모래-다이아톰 혼합 시료를 다양한 다이아톰 무게비에 따라 준비 후 실내 투수계수 시험을 수행하였다. 세번째로, 본 연구에서 얻은 실험결과와 방대한 데이터에 기반하여 제안된 투수계수 예측 모델을 비교하여 비표면적 관점에서 분석을 수행하였다. 분석 결과, 다이아톰 함량에 따른 투수계수 변화는 세가지 경향을 보여주었다: (i) 모래의 간극을 다이아톰이 채움으로써 일어나는 투수계수의 급격한 감소 구간, (ii) 다이아톰에 의하여 형성되는 간극의 크기가 지배적인 전이 구간, (iii) 다이아톰의 입자 표면을 따라 발생하는 동적 전단저항력 증가 구간. 본 연구에서는 다공성 입자 표면을 가지는 다이아톰이 해저지반의 유체 흐름에 미치는 영향을 비표면적 SS (i.e., drag force)과 간극비 e (i.e., pore size) 관점에서 분석하고 주어진 입자의 기본 물성치를 이용하여 단순화된 이론식을 통해 투수계수를 예측할 수 있음을 보여준다.
-
Physics-inspired and Data-driven Analyses of Fluid Flow in Seafloor Sediments
-

-
Development of Water Pressure-Compensated Self-Weighted Multiphysics Cone Penetration Apparatus for Investigation of Soft Offshore Sites
해상연약지반 탐사를 위한 수압보상형 자중관입식 다중물리 콘 관입시험기 개발
-
Juna Lee, Junghee Park
이준아, 박정희
- Offshore geotechnical projects require reliable design parameters for seabed structures such as wind turbine foundations, cables, tunnels, and pipelines, where such parameters …
해저공간에 대한 발전가능성이 높아지는 가운데 해저 지반구조물의 중요성이 증가하고 있다. 본 연구에서는 기존의 해저지반조사 방법들의 한계점을 개선하기 위해 수압보상형 자중관입식 다중물리 콘 …
- Offshore geotechnical projects require reliable design parameters for seabed structures such as wind turbine foundations, cables, tunnels, and pipelines, where such parameters must be estimated precisely and in an economical manner. However, conventional site investigation methods are sensitive to high pressure and are very expensive. This study proposes a water-pressure-compensated self-weighted multiphysics cone penetration apparatus for analyzing offshore soft ground. We designed a hydraulic compensation cone probe enabling high-resolution measurement of the resistance of the cone tip. The skin friction load cell designed in this study is separate from the cone tip module for pure skin friction measurements. A plastic circuit board (PCB) installed inside the body of the cone enables real-time data monitoring and storage during penetration. Furthermore, we conduct a preliminary laboratory test before field application of the multiphysics cone. The PCB successfully stored all measured data during the preliminary tests. The resistance of the cone tip appears to be higher in clay‒sand mixtures with a higher weight fraction of sand and captures the specimen heterogeneity. The resistance of the cone tip during the measurement evolves in three stages: The frictional resistance appears to be zero for very soft sediments. Acceleration data enable calculation of the cone inclination angle. Within the seafloor, the cone penetration rate is expected to exceed v = 2 cm/s, which will ensure combined undrained and unconsolidated conditions; therefore, the multiphysics cone apparatus can capture the resistance characteristics of the pure seafloor, which depend on the residual effective stress only under undrained and unconsolidated conditions. Indeed, the water-pressure-compensated self-weighted penetration multiphysics cone apparatus can be used for cost-effective and highly repeatable site investigation.
- COLLAPSE
해저공간에 대한 발전가능성이 높아지는 가운데 해저 지반구조물의 중요성이 증가하고 있다. 본 연구에서는 기존의 해저지반조사 방법들의 한계점을 개선하기 위해 수압보상형 자중관입식 다중물리 콘 관입시험기를 개발하였다. 본 연구에서 제안한 새로운 콘 관입시험기는 콘 팁 모듈과 주면마찰력 로드셀을 구조적으로 분리한 설계를 통해 선단저항력과 주면마찰력을 독립적으로 측정한다. 특히, 수압보상형 선단부 콘 팁 모듈은 해수면 수심에 따라 증가하는 정수압의 영향을 최소화하여 선단저항력을 평가하도록 설계되었다. 콘 시험기 내부에 가속도계를 설치하여 콘 관입경사를 파악할 수 있도록 하였다. 본 연구에서 제안한 콘 관입시험기의 현장 적용성 평가를 위해 점토 – 모래 혼합시료를 조성하여 콘 자중에 의한 관입 실험을 수행하였다. 실험결과, 선단저항력은 콘 관입에 따라 뚜렷하게 구분되는 3가지 경향을 보여주었고 선단저항력은 모래 비중이 높은 시료에서 더 크게 나타났으며, 혼합시료의 불균질성을 보여주었다. 주면마찰력은 매우 연약한 시료 조건으로 인해 거의 0으로 나타났다. 측정된 가속도계 데이터는 콘 관입경사를 판단하기 위해 매우 효과적인 정보를 제공한다는 것을 보여주었다. 본 연구에서 수행한 배수/비배수 분석 및 향후 목표로 하는 해저지반 천층부의 비압밀 특성을 고려하였을 때 수압보상형 자중관입식 다중물리 콘 관입시험기는 2cm/sec 이상의 관입속도에 독립적이며 잔류유효응력에 의해 결정되는 해저 연약지반의 강도특성을 효율적으로 평가할 수 있다고 판단된다.
-
Development of Water Pressure-Compensated Self-Weighted Multiphysics Cone Penetration Apparatus for Investigation of Soft Offshore Sites
-
-
Analysis of Long-term Compression Settlement Behavior of Embankment Materials with Various Fine Content
세립분 함량에 따른 성토재료의 장기압축침하 거동 분석
-
Seung-Jun Lee, Tea-Wan Bang, Jong-Nam Do, Wan-Jei Cho
이승준, 방태완, 도종남, 조완제
- Embankments and backfill ground above underground structures play a crucial role in transferring and supporting external loads. The interaction between the ground …
지중구조물 상부 성토 및 뒤채움 지반은 외부 하중을 전달하고 지지하는 역할을 수행하며, 구조물과 상호작용하여 안정성 및 성능 확보에 기여한다. 그러나 시간이 경과함에 …
- Embankments and backfill ground above underground structures play a crucial role in transferring and supporting external loads. The interaction between the ground and structure is essential for maintaining stability and performance. However, time-dependent creep settlement can severely affect structural integrity by causing deformation and cracking. As reports of these types of issues continue to increase, engineering interest in the long-term behavior of ground materials has increased markedly. This study identified applied load and fine content as major influencing factors based on an analysis of domestic cases and creep mechanisms. Large-scale compression tests were then performed on actual embankment materials. In addition, the applicability of major long-term settlement prediction methods was assessed using the test results. Analysis of the test data revealed that increased applied load and fine content resulted in greater creep deformation. Notably, under high-load conditions with 25% fine content, creep accounted for approximately 40% of the total deformation. These conditions led to significant discrepancies among settlement prediction methods for sandy soils, with potential long-term deformation exceeding the empirical prediction range of 1.1%. This suggests that even sandy materials meeting current standards may experience settlement beyond allowable limits, particularly in high-embankment scenarios. Consequently, a review of the adequacy of current design criteria and the implementation of stricter management standards are necessary to ensure long-term settlement stability.
- COLLAPSE
지중구조물 상부 성토 및 뒤채움 지반은 외부 하중을 전달하고 지지하는 역할을 수행하며, 구조물과 상호작용하여 안정성 및 성능 확보에 기여한다. 그러나 시간이 경과함에 따라 발생하는 지반의 Creep 침하는 구조물의 변형, 균열 발생 등 안정성에 심각한 영향을 미칠 수 있으며, 이러한 문제 사례가 지속적으로 보고됨에 따라 지반 장기거동 특성 및 그 영향에 대한 공학적 관심이 높아지고 있다. 이에 본 연구는 국내 사례 및 Creep 메커니즘 분석을 통해 하중과 세립분 함량을 주요 영향 인자로 파악하고, 실제 성토재료를 대상으로 대형 압축실험을 수행하였다. 또한, 실험 결과를 토대로 주요 장기 침하 예측법의 적용성을 검토하였다. 실험 결과, 재하 하중 및 시료 내 세립분 함량 증가는 Creep 변형을 증가시켰으며, 특히 고하중 및 세립분 25% 조건의 경우 전체 변형의 약 40% 정도가 Creep에 의해 발생하는 것으로 확인되었다. 이러한 조건에서는 사질토의 침하 예측 방법 간 편차가 크게 발생하였고, 일부는 경험적 예측 범위(1.1%)를 초과하는 장기 변형 가능성도 확인되었다. 이는 현행 기준을 충족하는 사질토 재료의 경우에도 고성토 조건 등에서 허용 한계 이상의 침하 발생 가능성을 나타내며, 장기 침하에 대한 안정성 확보를 위해 설계 기준의 적정성 검토 및 보다 엄격한 관리 기준이 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
-
Analysis of Long-term Compression Settlement Behavior of Embankment Materials with Various Fine Content
-
-
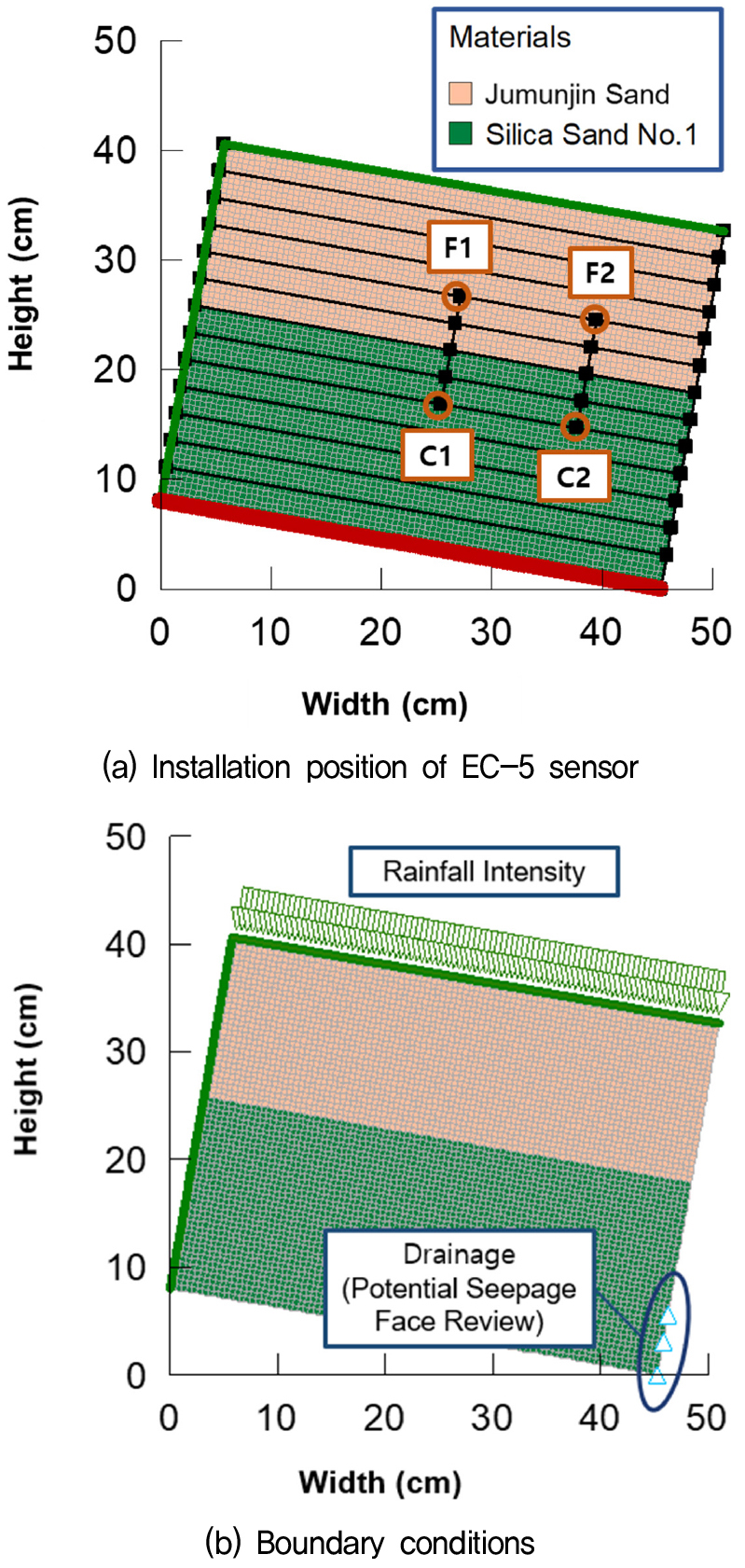
Infiltration Characteristics of Capillary Barrier Systems Using Model Tests
모형 토조 시험을 이용한 모세관 방벽 시스템의 침투 특성
-
Joon-Yeon Ko, Hyun-Su Park, Young-Min Kim, Byeong-Su Kim, Seong-Wan Park
고준연, 박현수, 김영민, 김병수, 박성완
- In geotechnical and civil engineering, capillary barrier systems (CBS) are widely utilized to prevent rainfall infiltration and improve the stability of soil …
모세관 방벽 시스템(Capillary Barrier System, CBS)은 토목 및 지반공학 분야에서 강우 침투를 제어하고 토양 구조물의 안정성을 향상시키기 위해 널리 사용되고 있다. 본 …
- In geotechnical and civil engineering, capillary barrier systems (CBS) are widely utilized to prevent rainfall infiltration and improve the stability of soil structures. This study evaluated the infiltration characteristics of CBS through small-scale model tests and infiltration analysis. The data conform that the performance of CBS is influenced by the slope angle and the thickness of the finer-grained layer, and that CBS can reduce rainfall infiltration on slopes. However, the performance of CBS decreased as the rainfall intensity increased. This study provides fundamental data for the design and optimization of CBS and suggests their potential application on slopes.
- COLLAPSE
모세관 방벽 시스템(Capillary Barrier System, CBS)은 토목 및 지반공학 분야에서 강우 침투를 제어하고 토양 구조물의 안정성을 향상시키기 위해 널리 사용되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 소규모 모형 토조 시험과 침투 해석을 통해 CBS의 침투 특성을 평가하였다. 경사 및 세립토층 두께가 CBS의 성능에 영향을 미치는 주요 인자임을 확인하였으며, CBS를 통하여 비탈면의 강우 침투를 억제할 수 있다는 것을 확인하였다. 하지만, 강우 강도가 증가할수록 CBS의 성능이 다소 저하되는 경향을 보였다. 본 연구에서는 CBS 설계 및 최적화를 위한 기초 데이터를 제공하였으며, 실제 비탈면에 강우 침투 방지 시스템으로서 CBS 적용에 대한 가능성을 제시하였다.
-
Infiltration Characteristics of Capillary Barrier Systems Using Model Tests
-
-
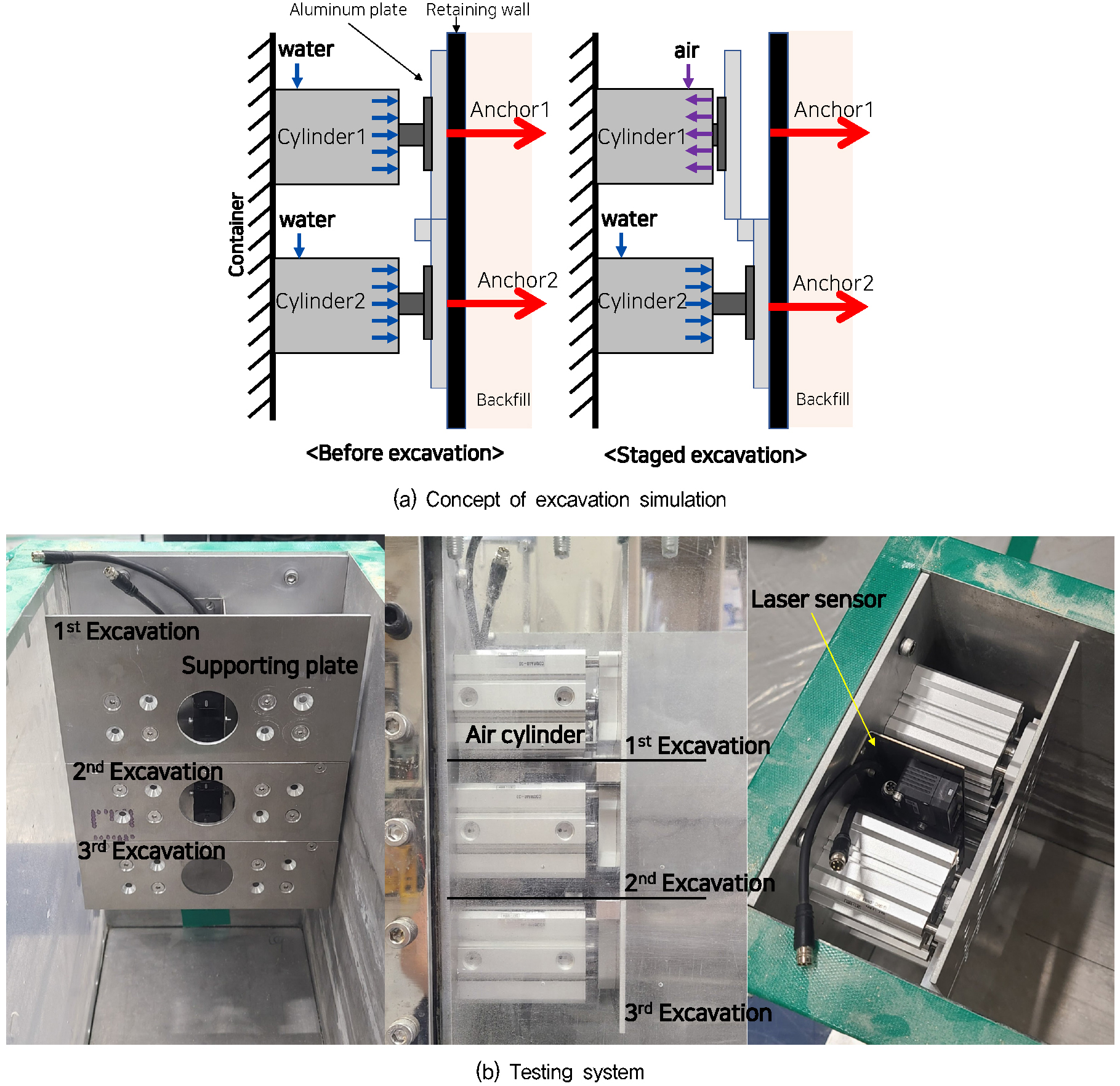
Evaluation of Ground Behavior Behind Retaining Walls During Excavation Using Centrifuge Model Tests
원심모형실험을 활용한 지하굴착시 배면지반 거동평가
-
Jae-Hyun Kim, Jong-Jeon Park, Jun-Young Ko, Ji-Seung Lee, Cheol-Ju Lee, Joon-Shik Moon
김재현, 박종전, 고준영, 이지승, 이철주, 문준식
- As the demand for underground space development increases, excavation activities in urban areas are increasing rapidly. Consequently, the settlement and deformation of …
지하공간 개발의 수요 증가로 인해 지하 굴착공사가 활발히 이루어지면서 굴착 중에 발생하는 배면지반의 침하 및 변형이 주요한 공학적 문제로 대두되고 있다. 지반 …
- As the demand for underground space development increases, excavation activities in urban areas are increasing rapidly. Consequently, the settlement and deformation of the retained ground during excavation have become critical geotechnical concerns. The influence zone that causes deformation in the retained ground is typically estimated using theoretical or empirical methods. However, these zones can vary significantly based on site-specific soil conditions and supporting structures, indicating the need for a quantitative analysis. This study conducted centrifuge model tests to evaluate the behavior of the retained ground during excavation. A staged excavation simulation system was developed to replicate excavation sequences within the centrifuge, and a series of tests were performed. The results quantified the influence zones for various ground conditions (sand, weathered rock) and support types (anchor, strut). The results revealed discrepancies between theoretical and empirical estimation methods for the influence zone under certain conditions. The study’s findings can be effectively applied in estimating excavation-induced influence zones.
- COLLAPSE
지하공간 개발의 수요 증가로 인해 지하 굴착공사가 활발히 이루어지면서 굴착 중에 발생하는 배면지반의 침하 및 변형이 주요한 공학적 문제로 대두되고 있다. 지반 굴착시 배면지반에 변형을 유발하는 영향범위는 일반적으로 이론 및 경험적 추정방법에 의존하고 있으나, 현장지반과 지지구조체 조건에 따라 영향범위가 다양하게 나타나고 있어 이에 대한 정량적 분석이 필요하다. 본 연구에서는 굴착시 배면지반의 거동을 평가하기 위해 원심모형실험을 수행하였다. 이를 위해 원심모형실험 중 단계굴착 모사가 가능한 실험시스템을 구축하고, 굴착과정에서 발생하는 지반거동을 실험적으로 평가하였다. 또한, 지반조건(모래, 풍화암)과 지지구조체 형식(앵커, 버팀보)에 따른 배면지반 영향범위를 산정하였다. 실험 결과, 영향범위에 대한 이론 및 경험적 추정방법과 실험결과가 특정 조건에서 차이를 보이는 것으로 확인되었다. 본 연구결과는 굴착시 영향범위를 추정하고 지하안전법에 따른 계측계획 수립시 유용하게 활용될 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
-
Evaluation of Ground Behavior Behind Retaining Walls During Excavation Using Centrifuge Model Tests
-
-
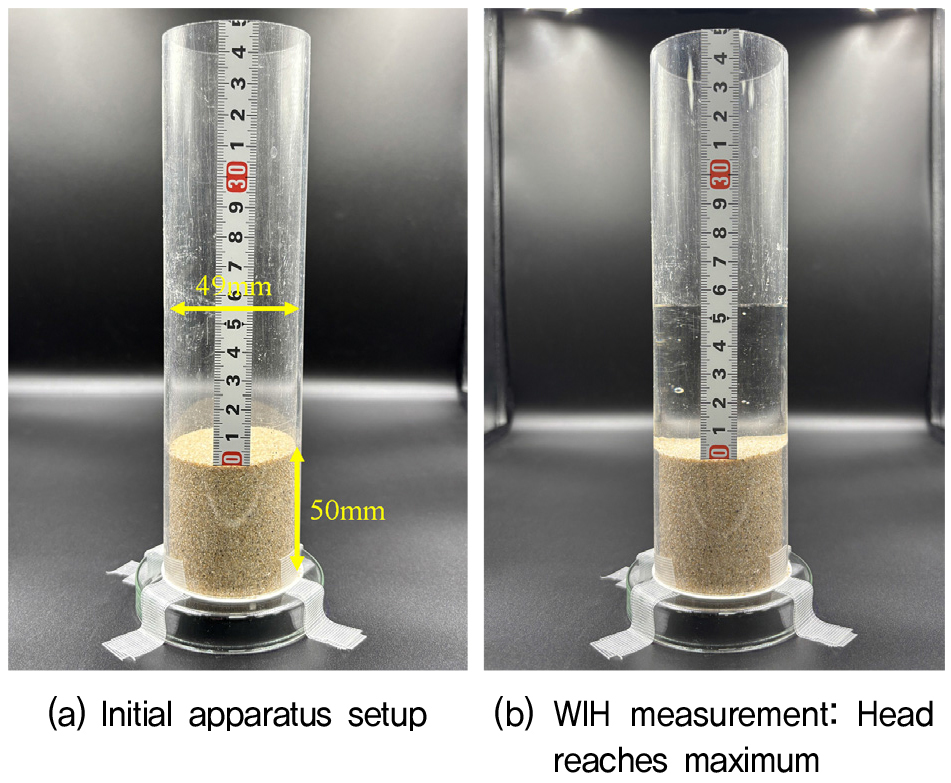
Evaluation of Hydrophobic and Mechanical Behavior of Hydrophobized Jumunjin Sand
소수화 처리된 주문진 표준사의 소수성 및 역학적 거동 특성 평가
-
Yeong-Ung Han, Jin-Hyung Kim, Jae-Hyun Kim, Seong-Wan Park, Byeong-Su Kim
한영웅, 김진형, 김재현, 박성완, 김병수
- As a countermeasure for preventing slope collapse caused by the infiltration of rainfall into the ground, hydrophobic ground materials can be applied …
국내의 사면 붕괴는 대부분 집중호우 시기에 발생한다. 본 연구는 강우 침투로 인한 사면 안정성 문제에 대응하기 위한 공법으로, 소수성 지반재료를 차수층으로 적용할 …
- As a countermeasure for preventing slope collapse caused by the infiltration of rainfall into the ground, hydrophobic ground materials can be applied as a water-proofing layer inside slopes. In this study, to obtain basic research data, Jumunjin standard sand was first hydrophobized and its hydrophobicity was evaluated. In the evaluation of the water infiltration head (WIH) for determining the hydrophobicity, the water-proofing performance of the sand was indicated by WIH = 10.24 cm H2O, the water drop penetration time was more than 3,600 s, and the contact angle was 134.6°, indicating that the material exhibits high hydrophobicity and water-proofing capability. A direct shear test was also performed to determine the mechanical characteristics of the hydrophobic Jumunjin sand, where the internal friction angles of the hydrophilic and hydrophobic materials were 40.3° and 32.3°, respectively (approximately 20% reduction). Therefore, for future application of hydrophobic barriers, the slope stability should be evaluated comprehensively, considering local strength reductions and the effect of blocking rainwater infiltration across the entire slope.
- COLLAPSE
국내의 사면 붕괴는 대부분 집중호우 시기에 발생한다. 본 연구는 강우 침투로 인한 사면 안정성 문제에 대응하기 위한 공법으로, 소수성 지반재료를 차수층으로 적용할 때의 공학적 특성을 평가했다. 소수성 주문진사는 소수성 평가를 위한 Water infiltration head(WIH) 시험에서 WIH = 10.24 cmH2O, Water drop penetration time(WDPT) 시험에서 3,600초 이상의 침투 저항, 그리고 접촉각 측정 시험에서 134.6°를 나타냈다. 또한 소수성 주문진사의 역학적 특성 파악을 위해 직접전단시험을 실시하여 친수성과 소수성 재료의 내부마찰각이 각각 40.3°과 32.3°가 얻어졌고 약 20% 감소한다는 것을 확인했다. 이러한 소수성 재료의 차수 성능 증가와 전단강도 저하 특성은 향후 소수성 차수층의 공학적 적용 시, 국부적인 강도 감소와 사면 전체의 강우 침투 차단 효과를 종합적으로 고려한 안정성 평가가 필요함을 시사한다.
-
Evaluation of Hydrophobic and Mechanical Behavior of Hydrophobized Jumunjin Sand
-
-
Analysis of the Behavior of Piled Raft Foundations Using Numerical Methods
수치해석을 통한 말뚝지지 전면기초의 설계 영향인자 분석
-
Chi-Young Yang, Ki-Chang Jeong, Kang-Il Lee
양치영, 정기창, 이강일
- This study investigated the load-settlement behavior and load-sharing characteristics of piled raft foundations to develop practical design guidelines. We conducted field measurements …
본 연구는 말뚝지지 전면기초의 거동 특성에 미치는 설계 인자별 영향을 정량적으로 분석하고, 이를 통해 설계인자별 가이드라인을 제시하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 이를 위해 …
- This study investigated the load-settlement behavior and load-sharing characteristics of piled raft foundations to develop practical design guidelines. We conducted field measurements and 3D numerical analyses using PLAXIS 3D, focusing on key parameters such as pile diameter, raft dimensions, material type, and embedment conditions. The results showed that increasing the width and thickness of the raft reduced settlement. In addition, pile diameters of 0.7–0.8 m achieved an effective balance between efficiency and cost. Steel piles demonstrated superior performance compared to PHC piles, whereas rock-socketed piles experienced less settlement and greater load sharing than those embedded in soil.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 말뚝지지 전면기초의 거동 특성에 미치는 설계 인자별 영향을 정량적으로 분석하고, 이를 통해 설계인자별 가이드라인을 제시하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 이를 위해 현장 계측과 수치해석(PLAXIS 3D)을 병행하여 말뚝지지 전면기초의 하중-침하 거동과 하중 분담 특성을 검토하였다. 특히 말뚝 직경, 기초 폭 및 두께, 말뚝 재료, 근입 조건 등 주요 변수의 변화에 따른 영향을 분석하였다. 해석 결과, 기초 폭 및 두께의 증가는 침하 안정성 확보에 유리하며, 0.7~0.8m 직경의 말뚝이 구조적 효율성과 시공성 측면에서 가장 적절한 것으로 나타났다. 또한 강관말뚝은 PHC 말뚝 대비 우수한 하중 분담 성능을 보였으며, 암반 근입 조건이 토사 근입 조건보다 침하량이 적고 하중 분담율이 높은 것으로 분석되었다.
-
Analysis of the Behavior of Piled Raft Foundations Using Numerical Methods
-

-
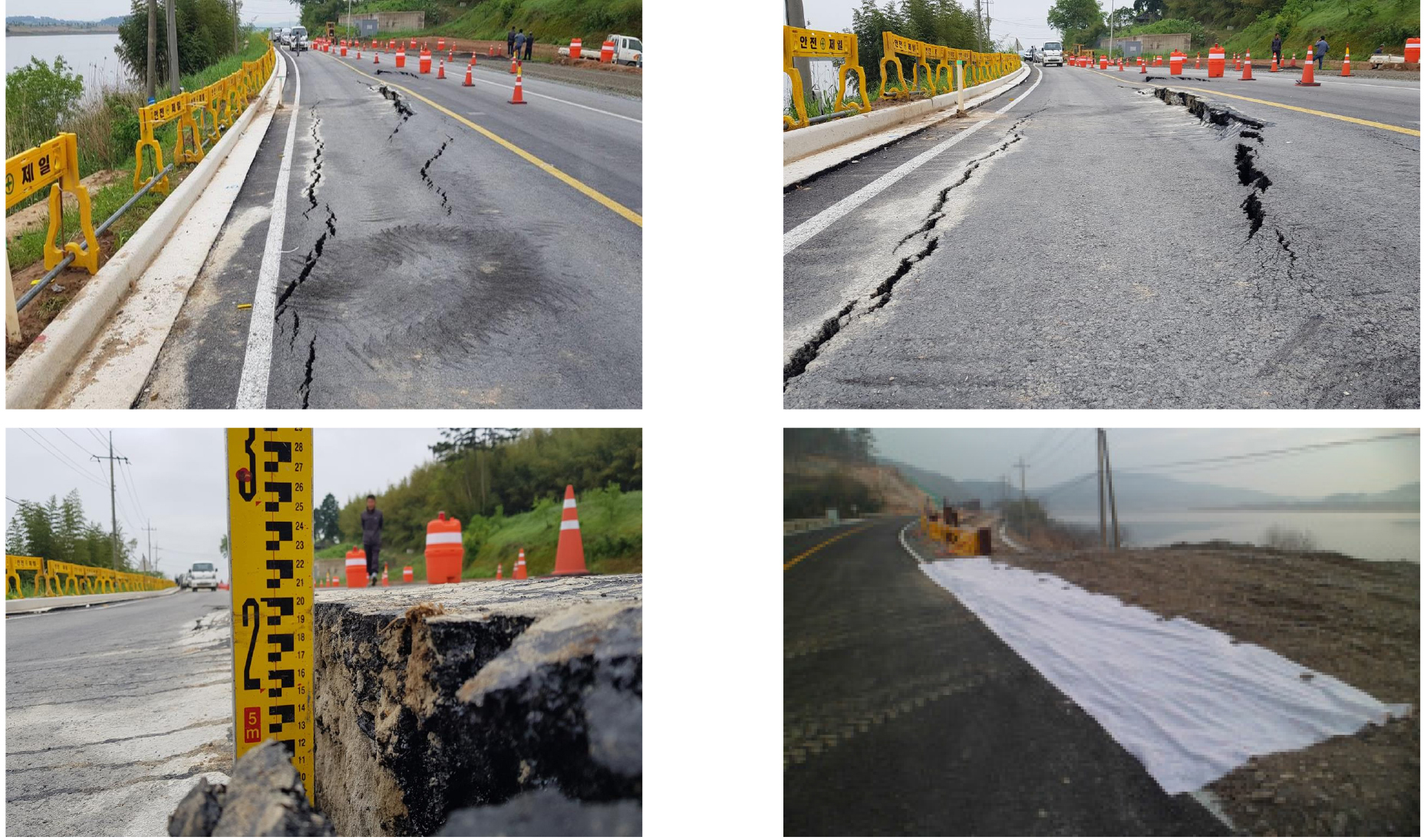
Analysis of Various Water Level Fluctuations for Achieving Long-Term Stability of River Levees
다양한 수위 변화에 대한 하천제방의 장기적인 안정성 분석
-
Jae-Hong Kim, Geon Nam, Beop-Jung Kim, Tae-Wan Kim
김재홍, 남건, 김법정, 김태완
- Maintaining and reinforcing river levees to respond to extreme rainfall caused by climate change remains a persistent engineering challenge. To advance these …
기후변화로 인한 극한강우에 대응하기 위하여 하천제방의 유지관리 및 보강공법은 지속적인 공학적 문제이다. 이러한 기술의 고도화를 위하여 저수지 및 하천제방과 같은 시설물을 대상으로 …
- Maintaining and reinforcing river levees to respond to extreme rainfall caused by climate change remains a persistent engineering challenge. To advance these technologies, analyses of flood defense structures, such as reservoirs and river levees, should be conducted by considering various failure modes. This study analyzes the behavioral characteristics of a river levee in Dasi-myeon, Naju-si, Jeollanam-do, which actually collapsed because of rapid drawdown of the water levels. The changes in the factor of safety over time were evaluated by analyzing the unsaturated seepage and slope stability under extreme water level variations, such as overtopping of the levee and rapid drawdown of flood-level water. In most river levee failures in Korea, reinforcements were primarily designed as a preventive measure to avoid recurrence, whereas long-term stability was not sufficiently considered. To achieve long-term stability of levees, implementing supplementary measures to address various rainfall-induced slope instability and additional reinforcements that can effectively block seepage into the levee body is essential.
- COLLAPSE
기후변화로 인한 극한강우에 대응하기 위하여 하천제방의 유지관리 및 보강공법은 지속적인 공학적 문제이다. 이러한 기술의 고도화를 위하여 저수지 및 하천제방과 같은 시설물을 대상으로 다양한 파괴유형을 고려한 해석이 수행되어야 한다. 본 연구에서는 실제 수위급강하(Drawdown)로 인해 붕괴가 발생한 전라남도 나주시 다시면의 하천제방을 대상으로 수위 변화에 따른 제체의 거동 특성을 분석하였다. 제방의 월류 및 홍수위에서의 수위급강하와 같은 극한 수위 변화를 대상으로 불포화 침투해석과 사면안정해석을 연계하여 시간에 따른 안전율 변화를 분석하였다. 국내 대부분 하천제방 현장 붕괴에 대한 조치는 재발생의 예방 차원에서 보강 설계가 주로 수행되며, 장기적인 안정성은 충분히 고려되지 않고 있다. 장기적인 제체 안정성을 확보하기 위해서는 비탈면에서 발생하는 여러 문제에 대한 보완뿐만 아니라 제체 내부로의 침투수를 효과적으로 차단할 수 있는 추가적인 보강대책이 함께 적용되어야 할 것이다.
-
Analysis of Various Water Level Fluctuations for Achieving Long-Term Stability of River Levees
-
-
Liquefaction Resistance of Loose Sand and Eco-Friendly Reinforcement Materials (GeoCem)
느슨한 사질토지반 액상화 저항특성 및 친환경 보강재(GeoCem) 연구
-
Wook Jun, Ui Chan Lee, Jongwon Jung
전욱, 이의찬, 정종원
- In major urban areas of Korea, the near-surface ground is largely composed of loose reclaimed and sedimentary deposits, which are highly susceptible …
국내 주요 도심지의 지표 부근은 대부분 느슨한 매립층 및 퇴적층으로 구성되어 있어 액상화(Liquefaction) 발생 가능성이 크다. 액상화 피해 대책으로 주로 적용되고 있는 …
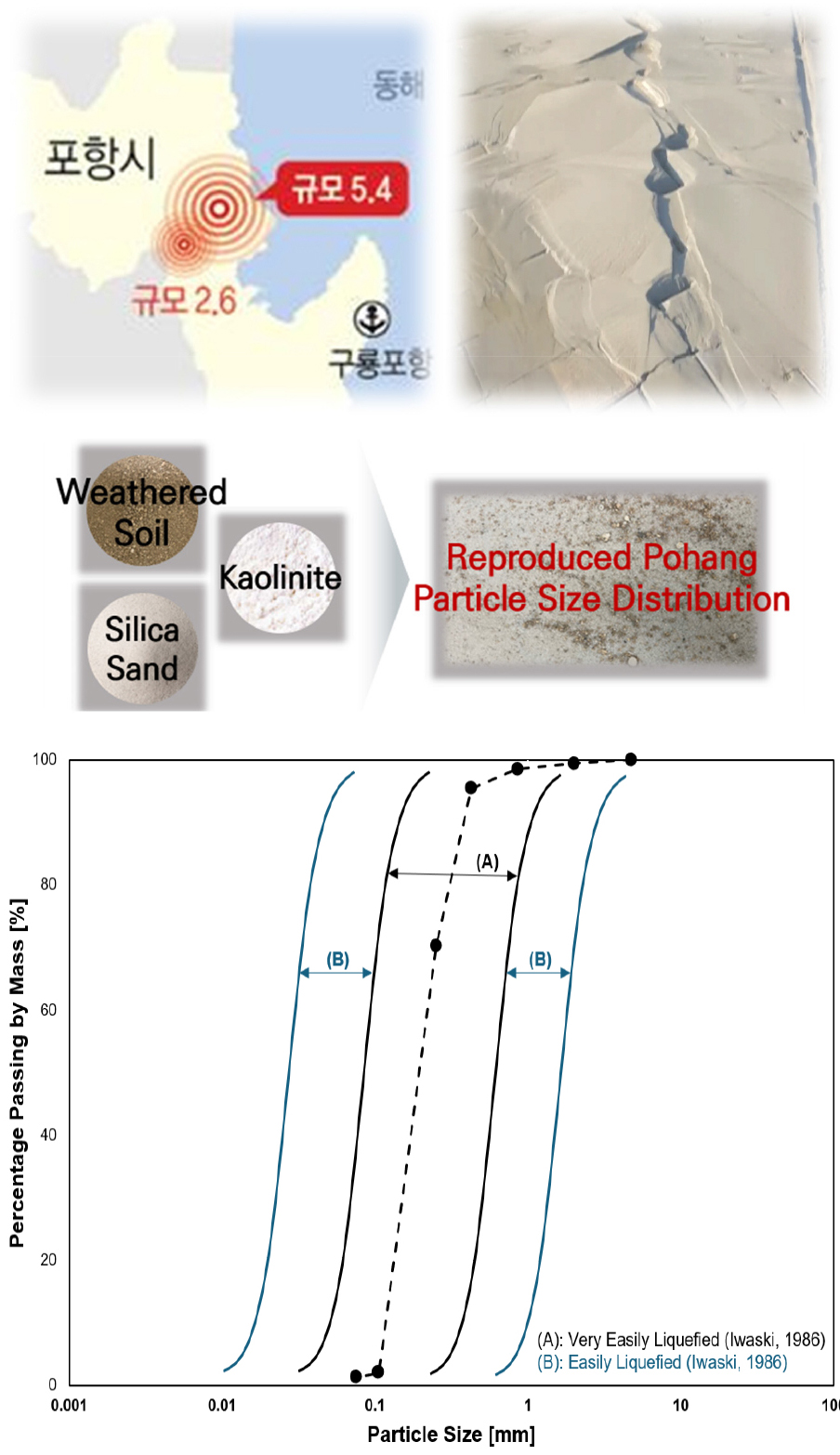
- In major urban areas of Korea, the near-surface ground is largely composed of loose reclaimed and sedimentary deposits, which are highly susceptible to liquefaction. Cement-based ground improvement methods, commonly applied as countermeasures, accelerate climate change through CO2 emissions and may cause groundwater and soil contamination. Thus, eco-friendly reinforcement materials for replacing cement are urgently required. In this study, cyclic shear tests were conducted on Pohang sand and cement-treated sand to quantitatively evaluate their liquefaction resistance. An eco-friendly reinforcement material that is more economical, environmentally sustainable, and exhibits superior liquefaction resistance compared with conventional cement was developed. The proposed material can effectively substitute cement in ground improvement, minimize cement consumption, and reduce CO2 emissions, thereby contributing significantly to carbon neutrality.
- COLLAPSE
국내 주요 도심지의 지표 부근은 대부분 느슨한 매립층 및 퇴적층으로 구성되어 있어 액상화(Liquefaction) 발생 가능성이 크다. 액상화 피해 대책으로 주로 적용되고 있는 시멘트계 보강공법은 이산화탄소(CO2) 발생 및 온실가스 증가로 기후변화를 가속하며, 지하수 및 토양 오염을 유발하므로 시멘트를 대체할 수 있는 친환경 보강재료 개발이 요구된다. 본 연구에서는 포항 모래와 시멘트 보강 모래를 대상으로 반복전단시험을 실시하여 액상화 저항특성을 정량적으로 평가하였으며, 기존에 사용되어온 시멘트보다 경제적이면서 친환경적이고 액상화 저항특성이 우수한 친환경 보강재료를 개발하였다. 본 연구에서 개발된 친환경 보강재료는 지반보강 시 시멘트 대신 사용되어 시멘트 사용량을 최소화하고 이산화탄소 배출량을 줄임으로써 탄소중립에 기여가 클 것으로 판단된다.
-
Liquefaction Resistance of Loose Sand and Eco-Friendly Reinforcement Materials (GeoCem)
-
-
Deep Learning-based Prediction of the Axial Bearing Capacity of PHC Auger-drilled Piles Using Dynamic Load Test Data
딥러닝 기반 동재하시험 자료를 활용한 PHC 매입말뚝의 연직지지력 예측
-
Kyu-Sun Kim
김규선
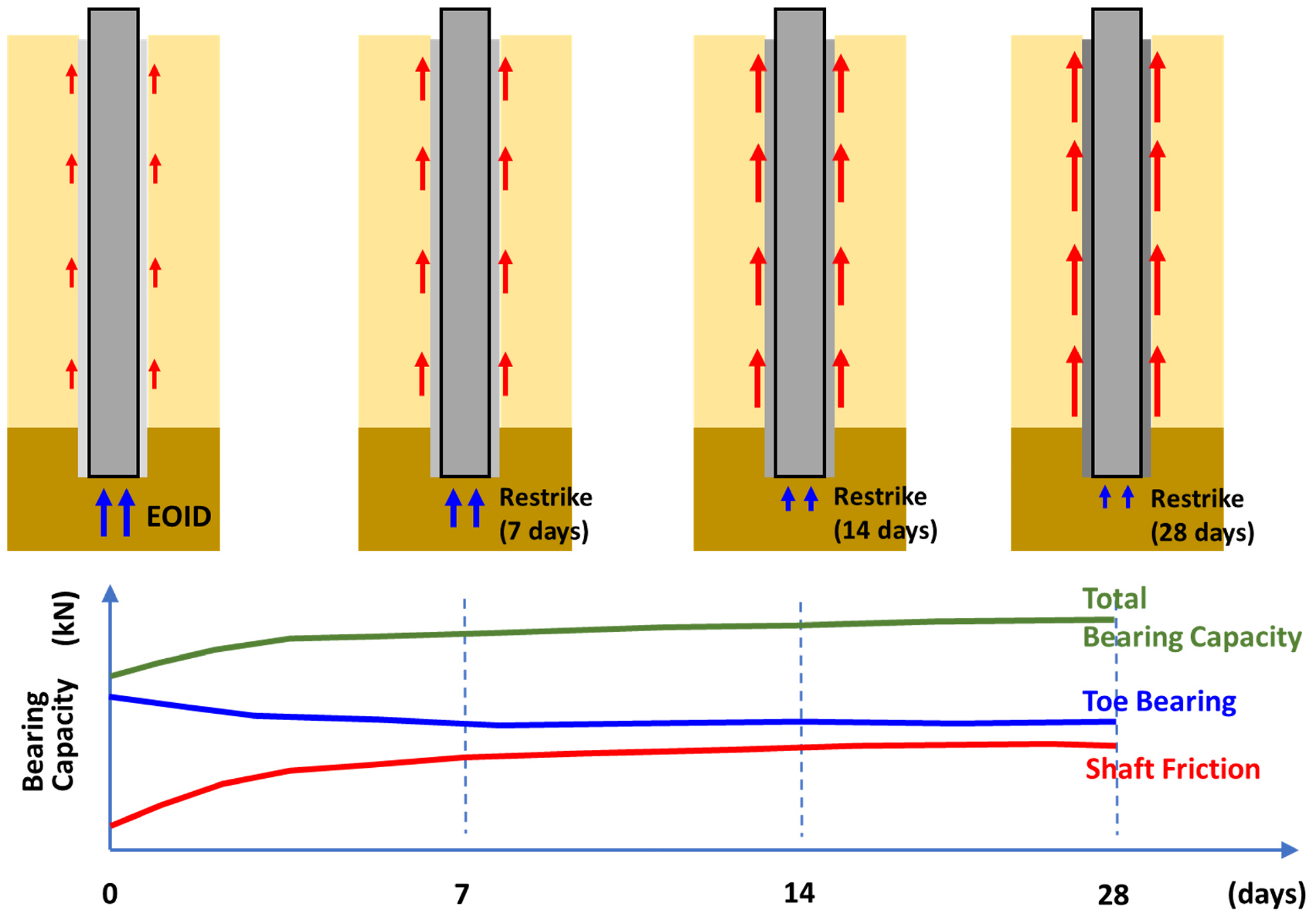
- In this study, a multi-output regression deep learning model that predicts the axial bearing capacity of PHC auger-drilled piles was developed using …
본 연구에서는 SDA 공법으로 시공된 PHC 매입말뚝의 연직지지력을 주면마찰력과 선단지지력으로 분리하여 예측하는 다중출력 회귀 딥러닝 모델을 개발하였다. 국내 다양한 조건에서 수집된 2,457개의 …
- In this study, a multi-output regression deep learning model that predicts the axial bearing capacity of PHC auger-drilled piles was developed using the SDA method by decomposing it into shaft friction and toe bearing capacity. A dataset of 2,457 dynamic load tests conducted under various conditions in Korea was used to train the deep learning model. The model was constructed with eight input variables, including pile specifications, ground conditions, driving parameters, and construction conditions, and three output variables: shaft friction, toe bearing capacity, and total bearing capacity. The accuracy of the trained deep learning model was R2=0.786 for shaft friction, R2=0.740 for the toe bearing capacity, and R2=0.825 for the total bearing capacity. Analyses of the influence of input variables on the output variables revealed that elapsed time and pile length were the dominant factors for shaft friction, elapsed time and pile diameter for the toe bearing capacity, and pile diameter and elapsed time for the total bearing capacity. The deep learning model, capable of efficiently predicting the bearing capacity characteristics of PHC auger-drilled piles exhibiting complex behavioral patterns, is expected to assist on-site construction managers in conveniently predicting suitable driving parameters and testing schedules that satisfy quality requirements, thereby facilitating effective auger-drilled pile construction and quality management.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 SDA 공법으로 시공된 PHC 매입말뚝의 연직지지력을 주면마찰력과 선단지지력으로 분리하여 예측하는 다중출력 회귀 딥러닝 모델을 개발하였다. 국내 다양한 조건에서 수집된 2,457개의 동재하시험 데이터셋을 딥러닝 학습에 이용하였으며, 말뚝제원, 지반조건, 항타조건, 시공조건 등의 8개 입력변수와 주면마찰력, 선단지지력, 총지지력의 3개 출력변수로 모델을 구성하였다. 학습된 딥러닝 모델의 정확도는 각각 주면마찰력 R2=0.786, 선단지지력 R2=0.740, 총지지력 R2=0.825로 나타났으며, 출력변수에 대한 입력변수의 영향성 분석결과, 주면마찰력은 경과시간과 말뚝길이, 선단지지력은 경과시간과 말뚝직경, 총지지력은 말뚝직경과 경과시간이 주요 영향인자로 파악되었다. 복잡한 거동을 나타내는 매입말뚝의 지지력 특성을 효율적으로 예측할 수 있는 딥러닝 모델은 현장 시공관리자가 목표 품질수준에 부합하는 항타조건 및 시험시기를 간편하게 예측하여, 효과적인 매입말뚝 시공 및 품질관리를 가능하게 할 것으로 판단된다.
-
Deep Learning-based Prediction of the Axial Bearing Capacity of PHC Auger-drilled Piles Using Dynamic Load Test Data
-
-
Shear Behavior of Soils with Microplastic Contents
미세플라스틱 혼입률에 따른 지반의 전단거동
-
Hyeonsu Yun, Seong-Kyu Yun, Gichun Kang
윤현수, 윤성규, 강기천
- Environmental pollution caused by microplastics has recently emerged as a global concern. In marine environments, microplastics are consumed by organisms and transferred …
최근 미세플라스틱에 의한 환경오염 문제가 심각하게 대두되고 있으며, 해양에서는 해양생물의 체내 축적과 먹이사슬 전이, 토양에서는 농경지와 매립지에서의 장기 잔류, 대기에서는 부유 및 …
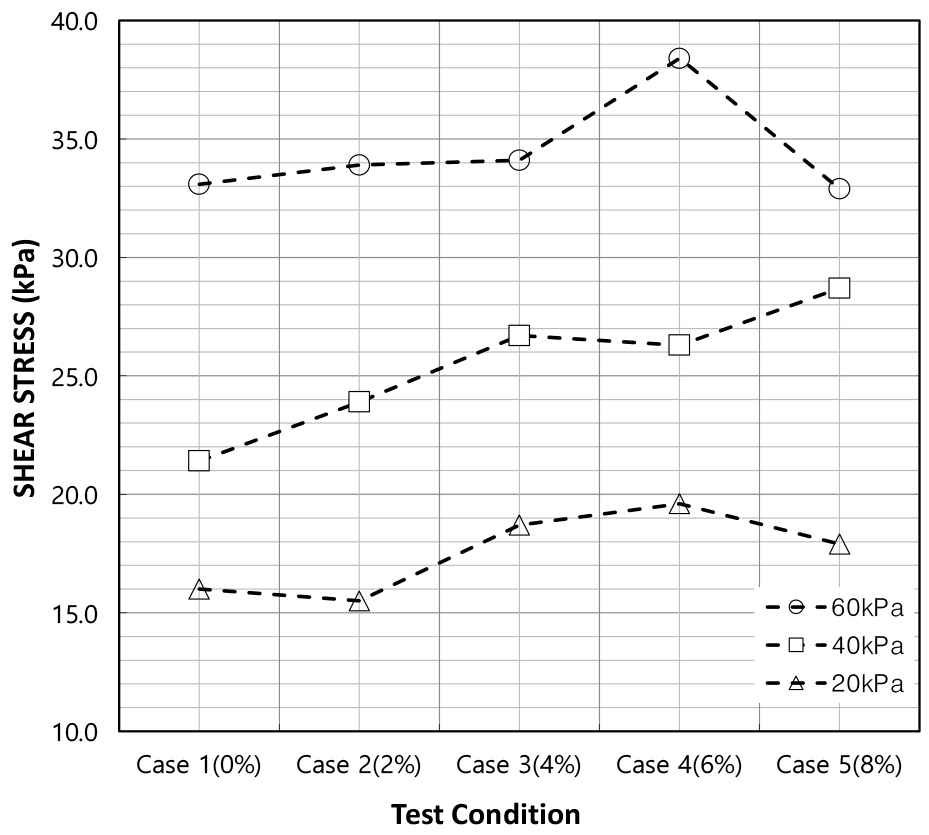
- Environmental pollution caused by microplastics has recently emerged as a global concern. In marine environments, microplastics are consumed by organisms and transferred through the food chain; in soils, they persist for long periods in agricultural fields and landfills; and in the atmosphere, they remain suspended and can be transported over long distances. Microplastics are small plastic particles (below 5 mm) found in various media, including air, water, and soil. Although extensive environmental studies have been conducted, research from a geotechnical engineering perspective remains limited. In this study, compaction and direct shear tests were performed on standard sand specimens prepared by mixing microplastics (0%–8%). The results revealed that shear strength increased at contents of 2%–6% but decreased at higher contents. These findings indicate that microplastic content can influence the shear strength of soils, highlighting the need to develop evaluation criteria that consider microplastic inclusion in geotechnical stability assessments.
- COLLAPSE
최근 미세플라스틱에 의한 환경오염 문제가 심각하게 대두되고 있으며, 해양에서는 해양생물의 체내 축적과 먹이사슬 전이, 토양에서는 농경지와 매립지에서의 장기 잔류, 대기에서는 부유 및 장거리 확산 등 다양한 형태의 오염이 보고되고 있다. 미세플라스틱은 크기 약 5mm 이하의 작은 플라스틱 입자로 공기, 물, 흙 등 다양한 환경에서 발견된다. 환경학적 연구는 많이 수행되고 있으나, 지반공학적 관점에서의 연구는 여전히 부족한 실정이다. 본 연구는 표준사에 미세플라스틱을 혼입(0~8%)하여 제작한 시료를 대상으로 다짐시험 및 전단시험을 수행하였다. 그 결과 2~6%의 경우 전단강도가 증가하였으나, 그 이상에서는 다시 감소하는 경향을 보였다. 이는 미세플라스틱 혼입률에 따라 지반의 전단강도에 영향을 미칠 수 있음을 의미하며, 지반 안정성 평가 시 미세플라스틱 함유 특성을 고려한 기준 마련이 필요하다고 판단된다.
-
Shear Behavior of Soils with Microplastic Contents
-
-
Development of Design Response Spectra for the Seismic Design of Lunar Structures Based on Apollo Meteoroid Impact Records
월면 구조물 내진설계용 설계응답스펙트럼 개발: 아폴로 유성체 충돌 기록 기반
-
Hyung-Ik Cho, Jin-Tae Han, Seokjung Kim, Jongkwan Kim
조형익, 한진태, 김석중, 김종관
- The lack of seismic design codes for moonquakes, a unique environmental hazard on the lunar surface, presents a significant engineering challenge for …
Apollo program, Lunar design response spectrum, Lunar seismic design, Meteoroid impact, Moonquakes
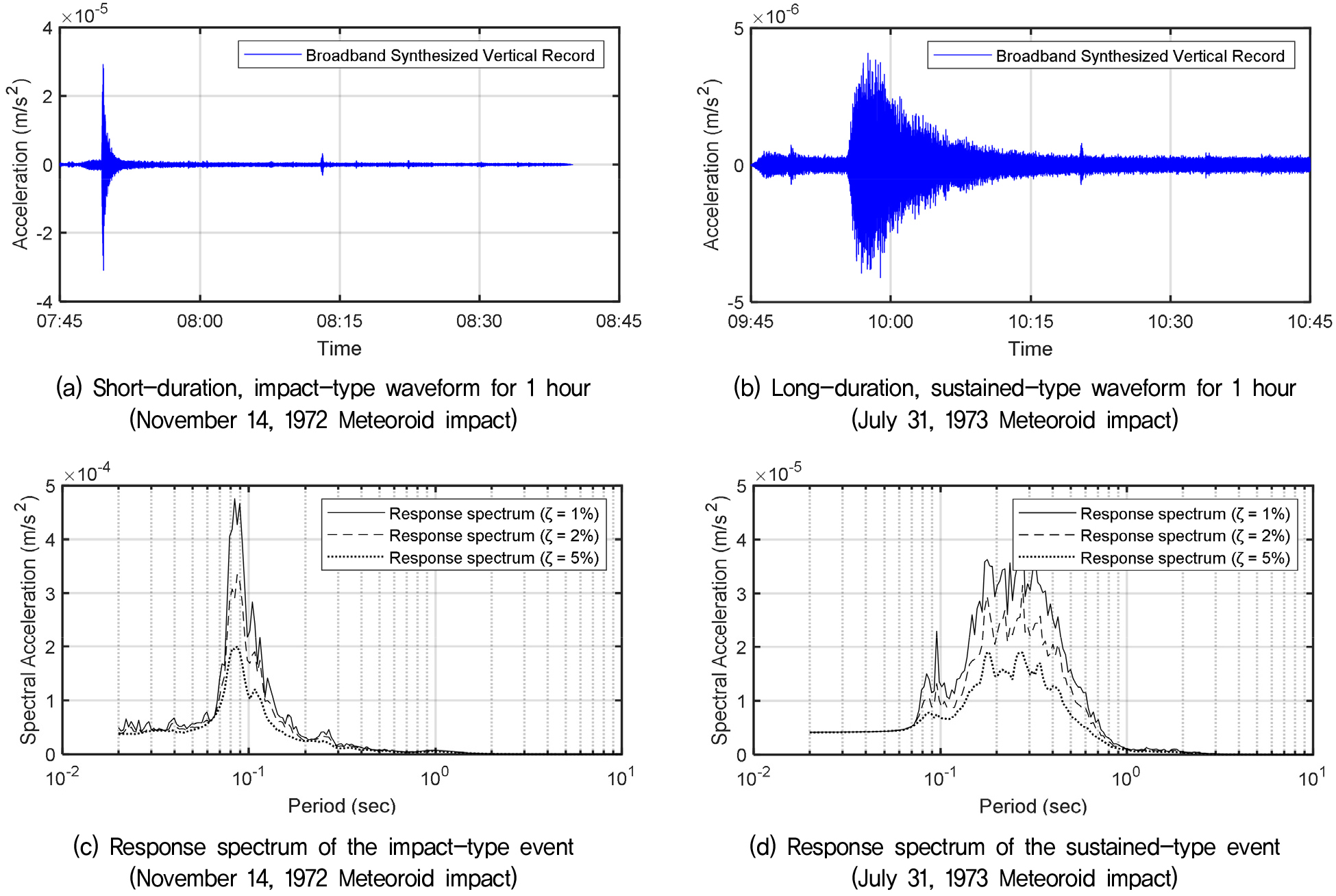
- The lack of seismic design codes for moonquakes, a unique environmental hazard on the lunar surface, presents a significant engineering challenge for ensuring the long-term stability of future structures. This study aims to develop lunar design response spectra for the lunar surface through a statistical analysis based on actual moonquake records acquired during the Apollo missions. Moonquake records exhibit waveform characteristics that markedly differ from those of earthquakes, owing to strong scattering and low attenuation. However, data available for analysis are extremely limited. This study first determines the vertical design response spectra (DRS) shape and the maximum spectral acceleration level based on a broadband synthesis of short-period and mid-period vertical records to rationally estimate the horizontal lunar ground motion, which is essential for seismic design. Subsequently, the horizontal DRS is derived by calculating the horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio from the mid-period seismometer records. The DRS presented in this study may serve as fundamental data for the preliminary seismic design and risk assessment of future lunar structures.
- COLLAPSE
Apollo program, Lunar design response spectrum, Lunar seismic design, Meteoroid impact, Moonquakes
-
Development of Design Response Spectra for the Seismic Design of Lunar Structures Based on Apollo Meteoroid Impact Records
-
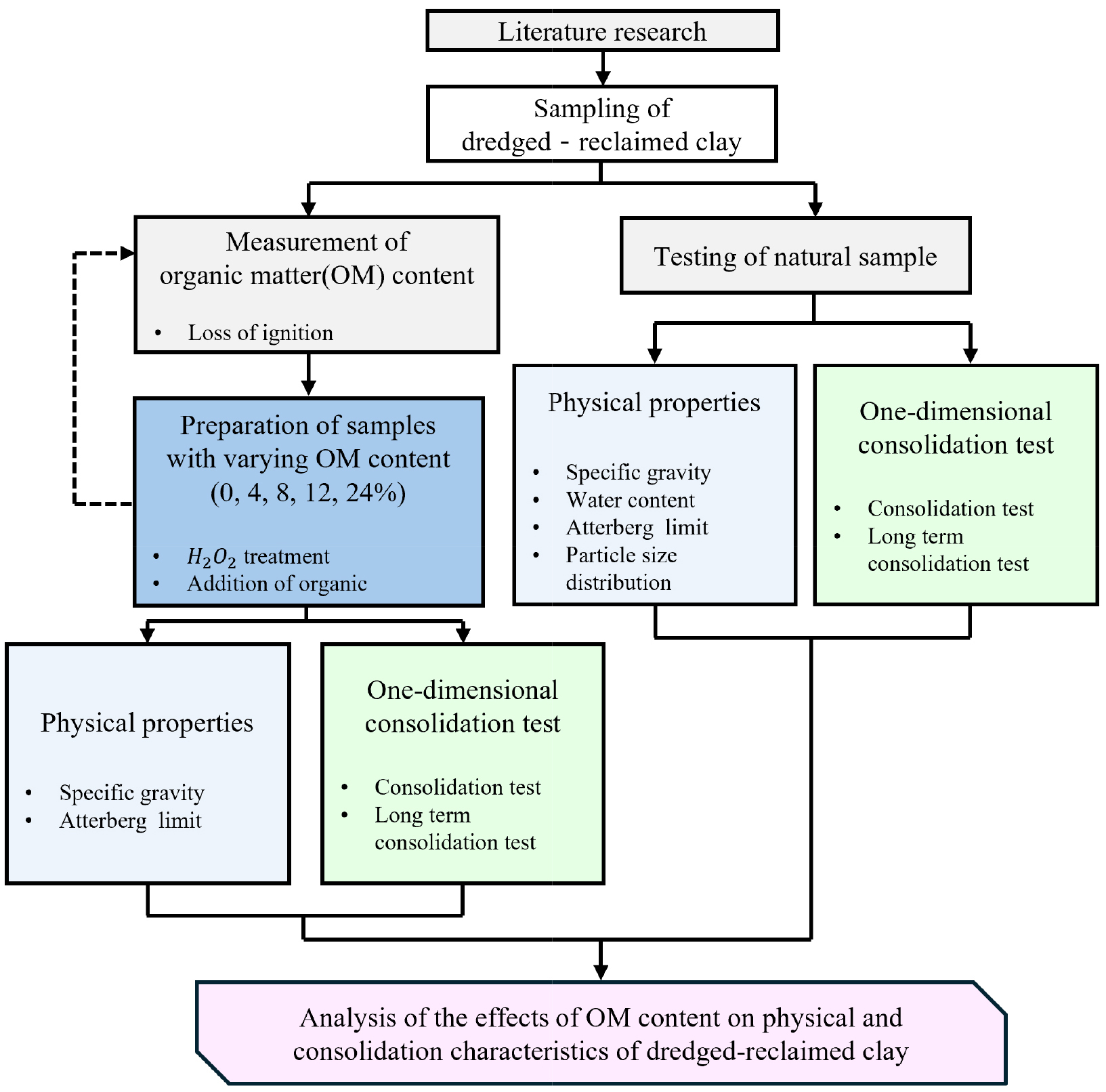
-
Analysis of Physical and Consolidation Characteristics of Dredged-Reclaimed Clayey Soils Based on Organic Matter Content
유기물 함량에 따른 준설매립 점토지반의 물성 및 압밀 특성 분석
-
Young-Ho Moon, Yoohyeon Kim, Hoon Song, Jongchan Kim, Yun-Tae Kim
문영호, 김유현, 송훈, 김종찬, 김윤태
- This study experimentally investigated the effects of organic matter (OM) content on the geotechnical and consolidation properties of dredged-reclaimed clay obtained from …
본 연구는 ○○항만에서 채취한 준설매립 점토를 대상으로 유기물 함량이 지반의 물성 및 압밀 특성에 미치는 영향을 실험적으로 규명하고자 수행되었다. 유기물 함량을 0%, …
- This study experimentally investigated the effects of organic matter (OM) content on the geotechnical and consolidation properties of dredged-reclaimed clay obtained from the ○○ port reclamation site in South Korea. Clay specimens were prepared with varying OM contents of 0%, 4%, 8%, 12%, and 24% and subjected to physical property tests (specific gravity, liquid limit, plastic limit, plasticity index) as well as one-dimensional consolidation tests (primary and secondary compression). The results indicated that an increase in OM content led to a decrease in specific gravity and a notable increase in both liquid and plastic limits. According to Casagrande’s plasticity chart, clay with 0%–8% OM was classified as CL (low-plasticity inorganic clay), whereas clay with ≥ 12% OM shifted to ML, OL, or OH zones, reflecting a significant increase in compressibility and plasticity. Consolidation test results showed a linear increase in both the compression index (Cc) and the secondary compression index (Cα) with increasing OM content. Notably, Cα values exceeded those reported in previous literature, indicating a high susceptibility to long-term settlement due to microstructural rearrangement and volumetric collapse associated with OM decomposition. Long-term secondary settlements for clay deposits of 30-m and 40-m thickness, with a field OM content of approximately 7.2%, would surpass the allowable residual settlement threshold (10 cm) within 6–8 years and 3–5 years, respectively. These findings underscore the critical role of OM in the long-term behavior of dredged-reclaimed soils and serve as important design data for smart port infrastructure constructed on high-OM ground.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 ○○항만에서 채취한 준설매립 점토를 대상으로 유기물 함량이 지반의 물성 및 압밀 특성에 미치는 영향을 실험적으로 규명하고자 수행되었다. 유기물 함량을 0%, 4%, 8%, 12%, 24%로 조절하여 시료를 제작하고, 물성 시험(비중, 액성한계, 소성한계, 소성도) 및 압밀 시험(일차 및 장기 압밀)을 실시하였다. 실험 결과, 유기물 함량이 증가할수록 입자 비중은 감소하고, 액성한계 및 소성한계는 뚜렷하게 증가하였다. 소성도표 분석 결과, 유기물 함량 0–8% 시료는 CL(무기질 저소성 점토) 영역에 분포하였으며, 12% 이상인 시료는 ML, OL, OH 등으로 분류되어 유기물이 흙의 소성과 압축성을 증가시키는 역할을 한다는 것을 알 수 있다. 또한, 압밀 시험 결과, 유기물 함량이 증가할수록 압축지수(Cc) 및 이차압축지수(Cα)가 선형적으로 증가하였고, 특히 이차압축지수의 증가폭은 기존 문헌보다 크게 나타나 장기 압밀 침하에 대한 민감도가 높음을 보여주었다. 이를 바탕으로 점토층의 이차압축 침하량을 예측한 결과, 실제 유기물 함량(약 7.2%) 조건에서 점토층이 30m 이상일 경우 6-8년 안에, 40m 이상일 경우 3-5년 안에 허용 침하량(10cm)을 초과할 가능성이 높은 것으로 분석되었다. 본 연구는 준설매립지의 유기물 함량이 지반 안정성과 장기 침하 거동에 미치는 영향을 정량적으로 제시하였으며, 스마트항만 등 고정밀 기반시설 설계 시 중요한 기초자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
Analysis of Physical and Consolidation Characteristics of Dredged-Reclaimed Clayey Soils Based on Organic Matter Content
-

-
Effect of Bentonite Content and Temperature on Electrical Conductivity of Sodium Bentonite Slurries
벤토나이트 함량 및 온도에 따른 소듐 벤토나이트 슬러리의 전기전도도 특성에 관한 실험적 연구
-
Seolhee Han, Sang Inn Woo
한설희, 우상인
- This study examined the correlation between the bentonite content and electrical conductivity of bentonite slurries and analyzed the effect of temperature variation …
본 연구는 벤토나이트 슬러리의 벤토나이트 함량과 전기전도도의 상관성을 규명하고, 온도 변화가 전도도 거동에 미치는 영향을 분석하였다. 실험 결과, 벤토나이트 함량이 증가할수록 전기전도도는 …
- This study examined the correlation between the bentonite content and electrical conductivity of bentonite slurries and analyzed the effect of temperature variation on the evolution of the conductivity. The electrical conductivity increased with the bentonite content but exhibited a nonlinear trend, contrary to the linear previously reported relationship. The observed trend is attributed to the combined effect of ion release, which increases the conductivity, and decreased ion mobility at high ion concentrations, which suppresses the conductivity. The conductivity also increased with temperature but in a nonlinear pattern that cannot be explained simply by a reduction in the viscosity. The derived thermoelectric coefficient (α) revealed a nonlinear correlation, reflecting the complex effect of the bentonite content on the temperature sensitivity. This study demonstrates that conductivity-based evaluation provides a faster and more objective alternative to the methylene blue test and can be applied under high bentonite content and variable temperature conditions. Furthermore, it holds important implications for extending conductivity-based techniques to quality control and field applications of cut-off materials.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 벤토나이트 슬러리의 벤토나이트 함량과 전기전도도의 상관성을 규명하고, 온도 변화가 전도도 거동에 미치는 영향을 분석하였다. 실험 결과, 벤토나이트 함량이 증가할수록 전기전도도는 상승했으나 기존의 선형 관계와 달리 비선형적 경향을 보였다. 이는 용출 이온 농도 증가가 전도도를 높이는 효과와, 높은 이온 농도에서 이동도가 저하되는 효과가 동시에 작용한 결과로 해석된다. 또한 온도 상승 시 전도도는 증가했지만 단순한 점성 감소로는 설명되지 않는 비선형적 거동을 나타냈다. 이를 정량화하기 위해 도출한 온도보정계수(α)는 비선형 상관성을 보여, 벤토나이트 함량이 전도도의 온도 민감도에 미치는 복합적 영향을 반영한다. 본 연구는 전기전도도를 활용한 벤토나이트 함량 평가 기법이 기존 메틸렌 블루 시험법보다 신속하고 객관적이며, 고함량 및 다양한 온도 조건에서도 적용 가능함을 시사한다. 이는 차수재 품질 관리와 현장 적용에서 전기전도도 기반 기법의 활용 가능성을 확장한다는 점에서 중요한 의의를 가진다.
-
Effect of Bentonite Content and Temperature on Electrical Conductivity of Sodium Bentonite Slurries
-
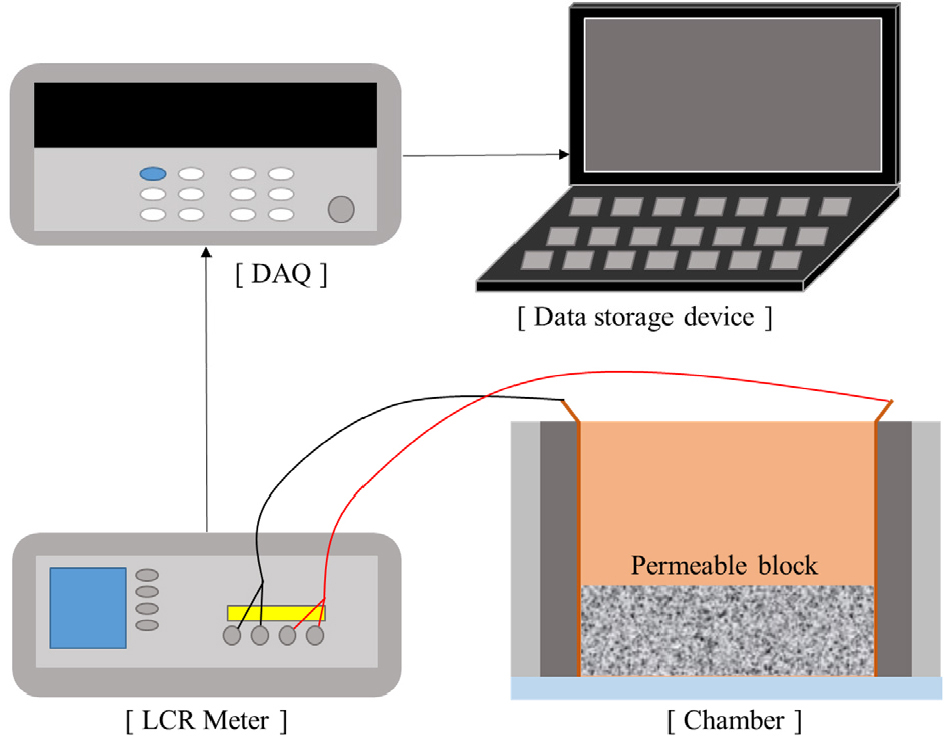
-
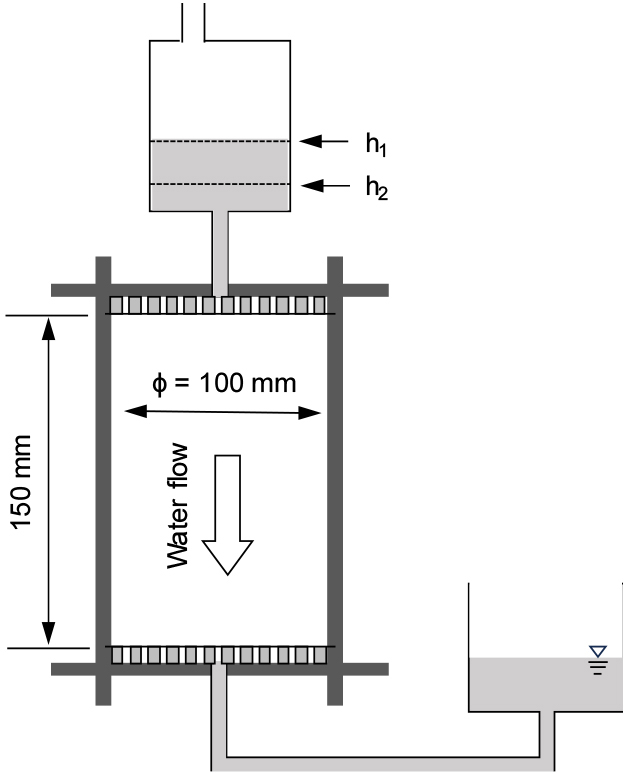
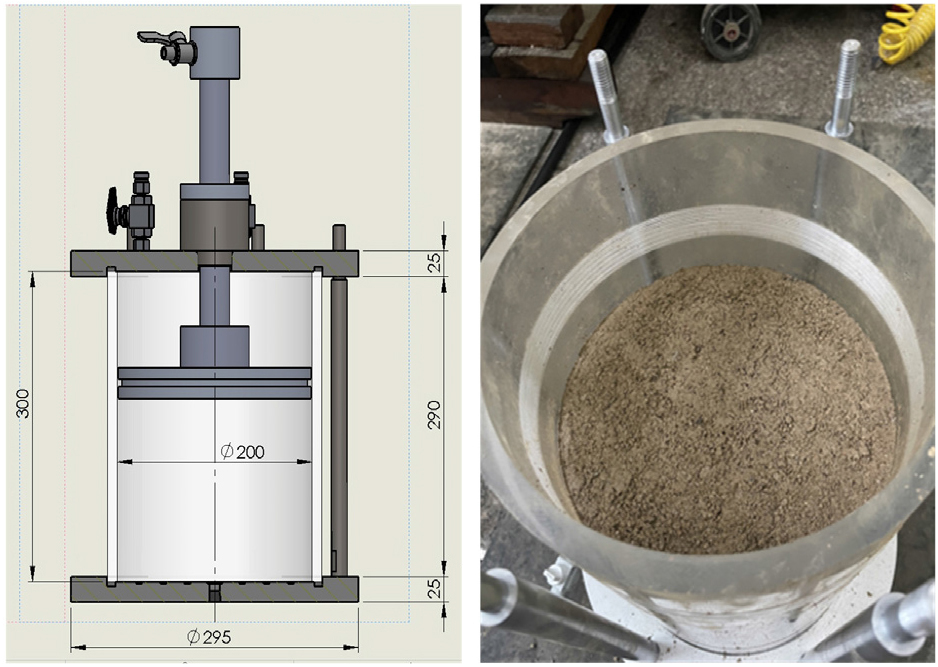
Analysis of Water Permeability of Pervious Blocks Using Electrical Resistivity
전기비저항을 이용한 투수블록의 투수성능 분석
-
Dong-Hyun Lee, Jun-Sik Park, Haeju Do, Jungmin Lee, Soonchul Kwon, Tae-Min Oh
이동현, 박준식, 도해주, 이정민, 권순철, 오태민
- Permeable blocks, used in stormwater management, contribute to improving urban water circulation and mitigating the island heating effect by reducing surface runoff …
빗물관리시설 중 하나인 투수블록은 유출수 저감과 우수 저류를 통해 도심지 물순환 개선 및 열섬현상 완화에 기여한다. 그러나 장기 사용 시 협잡물에 의해 …
- Permeable blocks, used in stormwater management, contribute to improving urban water circulation and mitigating the island heating effect by reducing surface runoff and storing rainwater. However, the permeability of these blocks decreases over time as the pores become clogged with debris, highlighting the need for continuous and nondestructive evaluation methods. This study aimed to nondestructively assess the evolution of the permeability of permeable blocks using electrical resistivity measurements, as an indirect indicator for estimating the degree of pore clogging. Two types of aggregates with different specific surface areas were used to fabricate the blocks and the binder content was adjusted to control the porosity. The relationship between the electrical resistivity and change in permeability was defined, enabling the use of the change in the resistivity as a metric of the permeability. The results confirmed that the electrical resistivity is an effective indicator for monitoring the performance degradation of permeable blocks.
- COLLAPSE
빗물관리시설 중 하나인 투수블록은 유출수 저감과 우수 저류를 통해 도심지 물순환 개선 및 열섬현상 완화에 기여한다. 그러나 장기 사용 시 협잡물에 의해 공극이 폐색되어 투수성능이 저하되므로, 성능을 지속적으로 모니터링할 수 있는 평가 기법이 필요하다. 본 연구에서는 전기비저항 측정을 이용하여 투수블록의 투수성능을 비파괴적으로 평가하고, 공극 폐색 정도를 간접적으로 판단하고자 하였다. 비표면적이 다른 두 종류의 골재로 투수블록을 제작하고, 결합재량을 달리하여 투수블록의 공극률을 조절하였다. 전기비저항 측정을 통하여 전기비저항과 투수블록의 투수성능의 상관관계를 분석하였으며, 전기비저항 값의 변화를 통해 투수성능을 판단하였다. 이를 통해 전기비저항이 투수블록의 성능 저하를 모니터링할 수 있는 유효한 지표임을 확인하였다.
-
Analysis of Water Permeability of Pervious Blocks Using Electrical Resistivity
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society











