-

-
Structural Stability Evaluation of Buried Concrete Pipes Under the Minimum Cover Depth Condition: Verification of Theoretical Formulas Based on Field-Measured Earth Pressure
최소 토피고 조건에서의 콘크리트 매설관 구조 안정성 평가: 현장 실측 토압을 통한 이론식 검증 중심으로
-
Jungwon Yun, Sukyu Lee, Ingun Park, Jongbae Park
윤정원, 이수규, 박인건, 박종배
- Reliable structural design of buried concrete pipes is critical for maintaining underground infrastructure subjected to external loads such as earth pressure and …
지중 매설 콘크리트관의 신뢰성 있는 구조 설계는 지하 기반 시설을 유지하기 위한 필수조건으로, 토압 및 윤압과 같은 외부 하중을 고려하여 수행된다. 현재 …
- Reliable structural design of buried concrete pipes is critical for maintaining underground infrastructure subjected to external loads such as earth pressure and wheel loads. Current design guidelines recommend a minimum cover depth (MCD) of 1 m; however, this does not sufficiently account for diverse pipe diameters (0.25–1.5 m). In this study, earth pressure and wheel loads acting on buried pipes were measured through field experiments under 1 m MCD, and theoretical formulas were verified based on the field experiment results. Subsequently, the safety factor (FS) was evaluated according to pipe diameter and bedding conditions under the MCD. The analysis results indicated that the FS decreased as the pipe diameter increased and that structural stability improved substantially when the ratio of cover depth to pipe diameter (H/D) exceeded 2. In particular, the required FS of 1.1 was satisfied when H/D ≥ 2 for sand bedding and H/D ≥ 1 for concrete bedding. Furthermore, minimum bedding angles required to ensure stability under sand bedding conditions were proposed: ≥60° for pipe diameters ≤ 500 mm, ≥90° for pipe diameters ≤ 1,000 mm, and ≥120° for pipe diameters ≤ 1,500 mm. This study quantitatively established structural stability criteria for buried concrete pipes based on the field-measured earth pressure, MCD, and H/D ratio, providing a practical foundation for revising current design standards and improving field applications.
- COLLAPSE
지중 매설 콘크리트관의 신뢰성 있는 구조 설계는 지하 기반 시설을 유지하기 위한 필수조건으로, 토압 및 윤압과 같은 외부 하중을 고려하여 수행된다. 현재 국내외 설계 지침에서는 최소 토피고를 1m 확보하도록 제시하고 있으나, 이는 국내에서 사용되는 다양한 관 직경(0.25~1.5m)의 영향을 충분히 반영하지 못하고 있다. 본 연구에서는 먼저 현장실험을 통해 최소토피고 1m 조건에서 매립관에 작용하는 토압 및 윤압을 측정하였으며, 현장실험 결과를 바탕으로 이론식을 검증하였다. 다음으로, 최소 토피고 조건에서 관 직경 및 기초 조건에 따른 안전율을 평가하였다. 분석 결과, 관 직경이 증가할수록 안전율이 감소하였으며, H(토피고)/D(직경) 비율이 2 이상인 경우 안정성이 현저히 향상되는 것으로 나타났다. 특히, 모래기초의 경우 H/D ≥ 2에서, 콘크리트기초의 경우 H/D ≥ 1에서 안전율 1.1을 확보할 수 있었다. 또한 관 직경별로 안정성을 확보하기 위한 최소 받침각을 제시하였으며, 직경 500mm 이하에서는 60° 이상, 1,000mm 이하에서는 90° 이상, 1,500mm 이하에서는 120° 이상(모래기초 기준)이 적절한 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구는 현장 실측 토압을 기반으로 퇴소 토피고 조건과 H/D 비율에 따른 구조적 안정성 기준을 정량적으로 제시함으로써, 향후 설계 기준 개정 및 실무 적용을 위한 실질적 근거를 제공하였다.
-
Structural Stability Evaluation of Buried Concrete Pipes Under the Minimum Cover Depth Condition: Verification of Theoretical Formulas Based on Field-Measured Earth Pressure
-
-
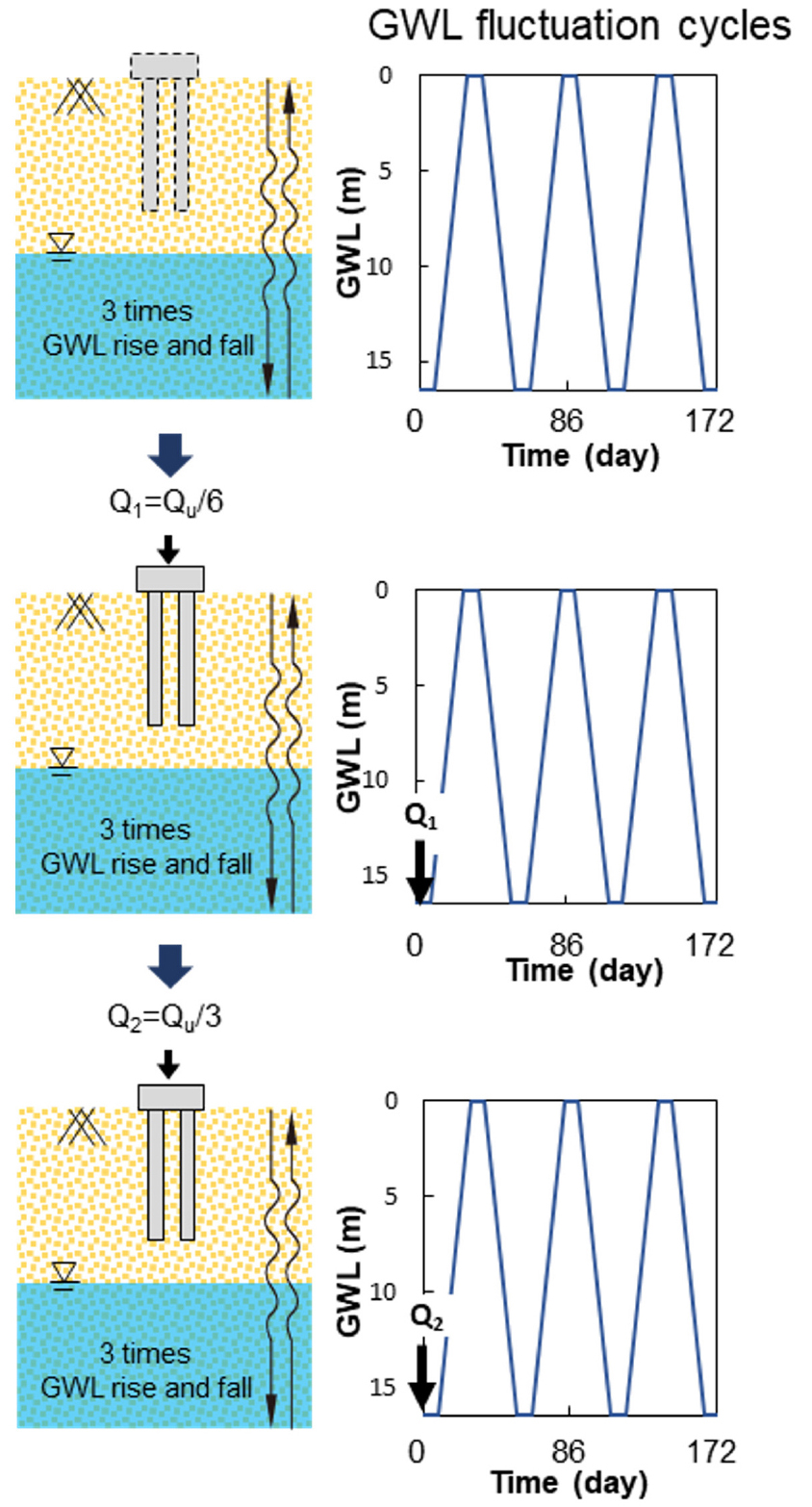
A Study on Settlement and Load Distribution Behavior of Piled Raft Foundations Due to Groundwater Fluctuations Using Centrifuge Tests
원심모형 실험을 이용한 지하수위 변동에 따른 사질토 지반에 설치된 말뚝지지 전면기초의 침하 및 하중 분담 거동에 관한 연구
-
Ji-Yeong Lee, Dong-Gun Nam, Jong-Hyeog Yoon, Aizhan Sagu, Myeong-Bin Kim, Min-Wook Kim, Jun-Hwan Lee
이지영, 남동건, 윤종혁, AizhanSagu, 김명빈, 김민욱, 이준환
- In this study, centrifuge tests were conducted to investigate the influence of fluctuating groundwater levels (GWLs) on the behavior of piled raft …
본 연구에서는 기후 변화 등으로 인한 지하수위(GWL) 변동이 사질토 지반에 설치된 말뚝지지 전면기초(Piled Raft Foundation)의 거동에 미치는 영향을 규명하기 위해 원심모형실험(centrifuge test)을 …
- In this study, centrifuge tests were conducted to investigate the influence of fluctuating groundwater levels (GWLs) on the behavior of piled raft foundations in sandy soil. To replicate the in situ stress conditions, the tests were performed under a centrifugal acceleration of 50g. The settlement (spr) and load-sharing ratio (αp) of the foundation were quantitatively analyzed during GWL successive rising and falling phases. The results revealed that as the GWL rose, the soil effective stress decreased and the matric suction in the unsaturated zone dissipated. This led to a considerable reduction in the shaft resistance and end-bearing capacity of the piles, triggering a “forced load redistribution” such that the superstructure load was transferred to the raft. The αp, which was initially 0.69, decreased drastically to 0.38 as the GWL approached the ground surface. Notably, irreversible hysteresis was observed; even when the GWL fell and the effective stress recovered, the load-sharing ratio remained constant owing to the residual contact pressure beneath the raft. Over three cycles of GWL fluctuation, cumulative settlement was the highest during the first cycle; with the behavior gradually converging to a steady state in subsequent cycles. These findings emphasize that piled raft foundations designed for areas with frequent GWL fluctuations must account for increased load demand on the raft and the potential for accumulated settlement during GWL rising phases.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 기후 변화 등으로 인한 지하수위(GWL) 변동이 사질토 지반에 설치된 말뚝지지 전면기초(Piled Raft Foundation)의 거동에 미치는 영향을 규명하기 위해 원심모형실험(centrifuge test)을 수행하였다. 실제 현장 응력 상태를 모사하기 위해 50g의 원심가속도 조건에서 실험을 진행하였으며, 지하수위의 상승 및 하강 주기에 따른 기초의 침하량(spr)과 하중 분담률(αp)의 변화를 정량적으로 분석하였다. 실험 결과, 지하수위가 상승함에 따라 지반의 유효응력 감소 및 불포화 영역의 흡입력(suction) 손실로 인해 말뚝의 주면마찰력과 선단지지력이 약화되었으며, 이로 인해 상부 하중이 전면기초로 전이되는 ‘강제적 하중 재분배’ 현상이 관찰되었다. 초기 약 0.69였던 αp는 지하수위가 지표면 부근까지 상승함에 따라 0.38까지 급격히 감소하였다. 특히, 수위가 하강하여 유효응력이 회복되더라도 이미 발생한 침하와 전면기초 하단의 접지압 고착화로 인해 하중 분담률이 회복되지 않는 비가역적인 이력 현상(hysteresis)이 확인되었다. 3회의 반복적인 수위 변동 결과, 첫 번째 주기에서 누적 침하의 상당 부분이 발생하였으며 주기가 반복될수록 거동이 특정 임계치로 수렴하는 양상을 보였다. 본 연구 결과는 지하수위 변동이 빈번한 지역의 말뚝지지 전면기초 설계 시, 수위 상승에 따른 전면기초의 분담 하중 증가와 누적 침하를 반드시 고려해야 함을 시사한다.
-
A Study on Settlement and Load Distribution Behavior of Piled Raft Foundations Due to Groundwater Fluctuations Using Centrifuge Tests
-

-
Dynamic Response Analysis of Railway Embankments Based on Korean Design Standards
국내 설계 기준을 반영한 철도 성토구조물의 동적 거동 분석
-
Hyunmin Song, Ji Hyeon Kim, Mintaek Yoo
송현민, 김지현, 유민택
- In this study, a finite-element-based numerical model was developed to analyze the dynamic behavior of railway embankment structures under seismic loading. The …
본 연구에서는 지진 시 철도 성토구조물의 동적 거동을 분석하기 위해 유한요소 기반의 수치 해석 모델을 구축하였다. 해석 모델 성토부는 국내 설계 기준에 …
- In this study, a finite-element-based numerical model was developed to analyze the dynamic behavior of railway embankment structures under seismic loading. The embankment model was constructed based on the standard slope of high-speed railway embankments specified in Korean design codes, while the underlying soil was modeled under various conditions based on Korean ground classification standards. Dynamic analyses were conducted using OpenSees by varying the bedrock depth and the shear wave velocity of the soil layers. The dynamic behavior of the embankment structure was evaluated primarily based on settlement at the embankment crest. The analysis results indicate that embankment settlement increases with increasing thickness of the underlying soil layer and decreasing shear wave velocity. In addition, the frequency characteristics of the input ground motion were found to have a substantial impact on the dynamic response of the railway embankment.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 지진 시 철도 성토구조물의 동적 거동을 분석하기 위해 유한요소 기반의 수치 해석 모델을 구축하였다. 해석 모델 성토부는 국내 설계 기준에 따른 고속철도 성토 비탈면의 표준 경사를 반영하였으며, 하부 토층 지반은 국내 지반 분류 기준을 반영하여 다양한 조건별 해석 모델을 구축하였다. OpenSees를 활용하여 기반암 깊이와 토층 전단파 속도를 달리한 다양한 조건에서 동적 해석을 수행하였으며, 성토 상부에서의 침하량을 도출하여 성토 구조물의 동적 거동을 분석하였다. 그 결과, 하부 토층의 두께가 증가하고 전단파 속도가 감소할수록 침하량이 증가하였으며 지진파의 주파수 특성 또한 큰 영향을 미치는 것으로 확인되었다.
-
Dynamic Response Analysis of Railway Embankments Based on Korean Design Standards
-

-
Evaluation of Hydrophobic and Mechanical Behavior of Hydrophobized Granulated Blast Furnace Slag
소수화 처리된 모래질 수재슬래그의 소수성 및 역학적 거동 특성 평가
-
Yeong-Ung Han, Jin-Hyung Kim, Min-Jun Baek, Seong-Wan Park, Byeong-Su Kim
한영웅, 김진형, 백민준, 박성완, 김병수
- The increasing frequency of extreme rainfall events driven by climate change, together with the decreasing availability of natural aggregates, highlights the urgent …
기후 변화에 따른 집중호우로 야기되는 비탈면 붕괴와 천연 골재 수급 감소 문제는 수리적·역학적 특성을 동시에 만족하는 지속가능한 대체 지반 재료 개발의 필요성을 …
- The increasing frequency of extreme rainfall events driven by climate change, together with the decreasing availability of natural aggregates, highlights the urgent need for sustainable geotechnical materials that can satisfy both hydraulic and mechanical performance requirements. This study investigates the engineering applicability of granulated blast furnace slag (GBFS), an industrial byproduct, after hydrophobic treatment for use as an impervious barrier layer in geotechnical structures. The hydrophobized GBFS exhibited excellent water repellency, with a water droplet penetration time exceeding 3,600 s (classified as “extremely water repellent”) a contact angle of up to 134.5° depending on the relative density, and a water infiltration head of 9.04 cm H2O. Direct shear tests revealed that the hydrophobic surface coating reduced interparticle interlocking, lowering the internal friction angle from 45.3° to 36.4°. Nevertheless, the final shear strength exceeded the standard design criterion for retaining wall foundations (ϕ > 35°), indicating sufficient mechanical stability without additional reinforcement. The results demonstrate that hydrophobized GBFS can satisfy both impermeability and geotechnical strength requirements, establishing it as a sustainable, high-performance substitute for natural aggregates in impervious layers and foundation ground materials.
- COLLAPSE
기후 변화에 따른 집중호우로 야기되는 비탈면 붕괴와 천연 골재 수급 감소 문제는 수리적·역학적 특성을 동시에 만족하는 지속가능한 대체 지반 재료 개발의 필요성을 높이고 있다. 본 연구에서는 산업부산물인 고로 수재슬래그에 주목하였고, 비탈면으로의 강우 침투 문제에 대응하기 위해 이 재료에 소수성을 부여하여 비탈면 내의 불투수성 차수층으로 활용하기 위한 공학적 특성을 평가하였다. 본 연구에서의 소수성시험 결과로부터, 소수화 처리된 수재슬래그는 물 침투 수두(WIH) 9.04cmH2O, 물방울 침투 시간(WDPT) 3,600초 이상의 극한 소수성 등급과 상대밀도에 따른 접촉각 측정 시험에서 최대 134.5°의 우수한 소수 성능을 나타냈다. 한편, 직접전단시험 결과로부터, 토립자 표면의 소수화 코팅으로 인해 입자 간 맞물림 효과가 감소하여 내부마찰각이 45.3°에서 36.4°로 약 20% 저하되었으나, 소수성재료의 감소된 내부마찰각은 국내의 도로 옹벽의 설계 기준(35°)을 상회하여 별도의 보강없이도 구조적 안정성을 확보할 수 있음을 확인하였다. 이러한 결과는 소수성 수재슬래그가 방수 성능과 역학적 성능을 동시에 만족시키며, 사면 차수층 및 기초지반용 재료로서 천연 골재를 대체할 수 있는 지속 가능한 고성능 지반 재료임을 입증하였다.
-
Evaluation of Hydrophobic and Mechanical Behavior of Hydrophobized Granulated Blast Furnace Slag
-

-
Analysis of Particle Loss in Granular Soils According to Flow Velocity Due to Internal Erosion
지반 내 유속에 따른 내부침식 기반 유실 입자량 분석
-
Haeju Do, Tae-Min Oh, Dong-Woo Ryu
도해주, 오태민, 류동우
- In recent years, the frequency of ground subsidence incidents resulting in human casualties has increased, leading to heightened societal and academic attention …
최근 지반함몰로 인한 인명 피해의 잦은 노출로 인해 지반함몰 현상 및 내부침식 현상의 발생 메커니즘에 대한 관심과 연구 수요가 증대되고 있다. 관련 …
- In recent years, the frequency of ground subsidence incidents resulting in human casualties has increased, leading to heightened societal and academic attention to the mechanisms underlying such phenomena. Despite this growing interest, previous studies have primarily employed numerical simulations or small-scale model tests, which have inherent limitations in realistically reproducing field conditions. Notably, the physical characteristics of the ground, particularly the particle size distribution and the velocity of infiltrating water, have been identified as critical factors influencing internal erosion mechanisms. This study quantitatively evaluates soil particle loss under varying fine content and hydraulic velocities through a series of controlled laboratory-scale internal erosion experiments. The results demonstrate that as flow velocity increases, both fine and coarse particles exhibit a corresponding increase in discharge quantity. Moreover, the sensitivity of particle loss to changes in velocity varies depending on the fine content of the specimen. The experimental apparatus and findings presented in this study are expected to provide a foundational basis for the quantitative assessment of internal erosion mechanisms and contribute to the development of predictive models and mitigation strategies for subsurface instability.
- COLLAPSE
최근 지반함몰로 인한 인명 피해의 잦은 노출로 인해 지반함몰 현상 및 내부침식 현상의 발생 메커니즘에 대한 관심과 연구 수요가 증대되고 있다. 관련 선행 연구 대부분이 수치해석을 기반으로 하거나 소규모의 모형실험이 대부분인 실정이다. 한편, 내부침식 발생에는 지반의 물리적 특성이 중요한 인자로 작용한다. 특히, 지반의 입도와 지반을 통과하는 물의 유속은 내부침식의 메커니즘과 밀접한 상관관계를 가진다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 실험실 규모의 내부침식 모사 실험을 통해 지반 입도(작은 입자 함량)와 물의 유속에 따른 지반 입자 유출량을 분석하여 내부침식 현상을 정량적으로 분석하고자 하였다. 실험 결과, 유속이 증가할수록 작은 입자 및 큰 입자의 유출량이 모두 증가하는 경향을 보였다. 또한 작은 입자의 함량에 따라 유속에 대한 유출 민감도 차이를 보였다. 본 연구에서 제안한 실험 장치와 결과는 지반 내부침식 메커니즘의 정량적 해석과 피해 예측, 그리고 향후 방지 대책 수립을 위한 기초자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Analysis of Particle Loss in Granular Soils According to Flow Velocity Due to Internal Erosion
-
-
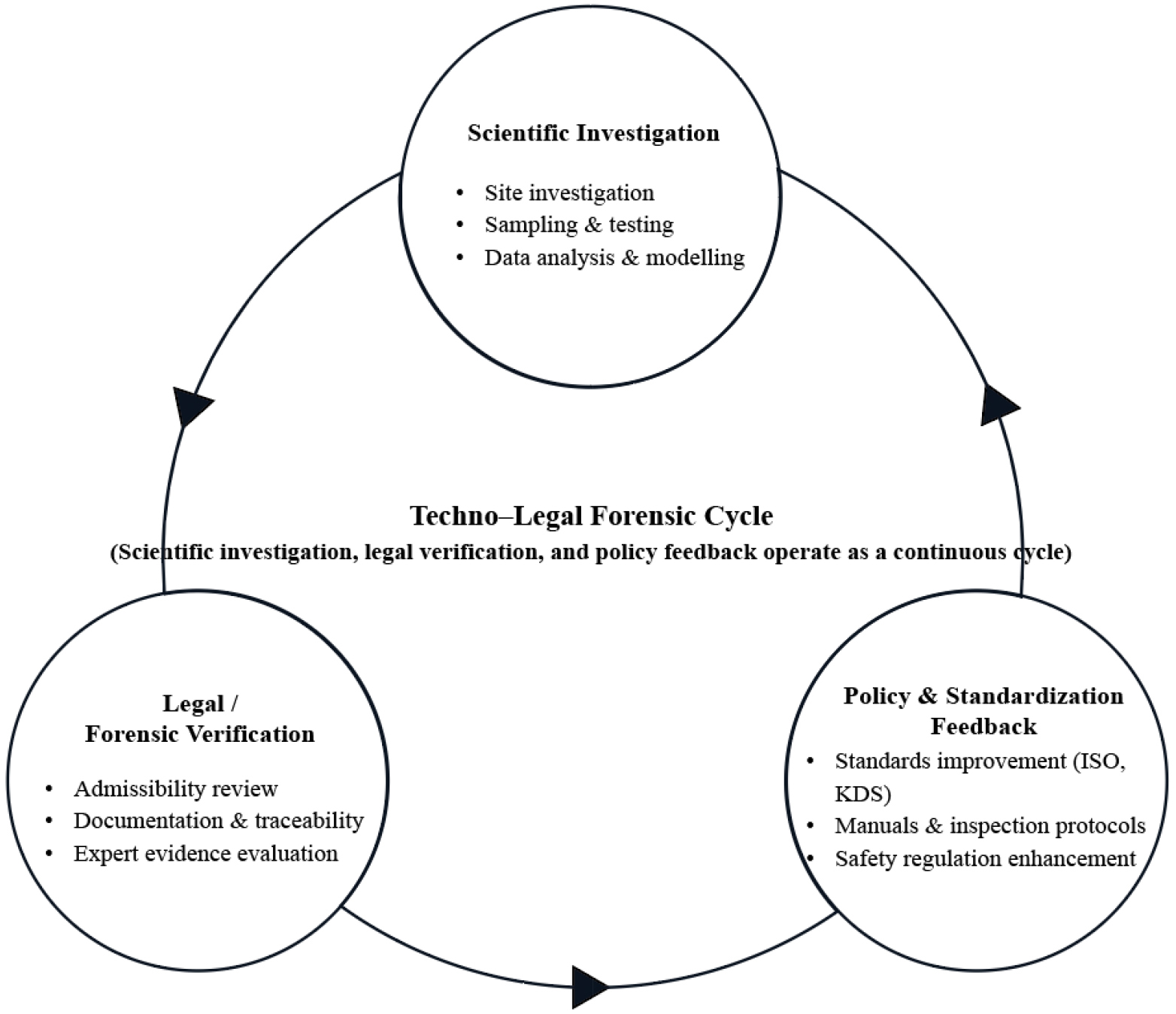
Standardization Framework for Forensic Investigation of Construction Accidents
건설사고 조사의 포렌식 표준화 체계에 관한 연구
-
Bon-Min Gu, In-Hwan Son, Kwang-Bin Kim, Jong-Moon Kim, Seoung-A Bang
구본민, 손인환, 김광빈, 김종문, 방승아
- This study examines the structural limitations of the current investigation framework for construction-related accidents in Korea and evaluates the need to establish …
본 연구는 국내건설 관련 사고에 대한 조사체계의 구조적 한계를 진단하고, 포렌식 기반 표준화 체계 구축의 필요성을 고찰하였다. 현행 조사체계는 발주기관·시공사·감리·행정기관 간 역할이 …
- This study examines the structural limitations of the current investigation framework for construction-related accidents in Korea and evaluates the need to establish a forensic-based standardization system. The existing investigation framework is fragmented across project owners, contractors, supervising engineers, and administrative authorities, which limits objectivity and consistency in identifying accident causes and determining responsibility. This fragmented structure often leads to duplicate investigations and procedural delays, resulting in prolonged disputes and increased socioeconomic costs. To address these challenges, this study proposes the adoption of a techno-legal construction forensic model that integrates technical evidence acquisition procedures with judicial processes. Furthermore, key components for improving the reliability and efficiency of construction accident investigations are identified, including ISO-based standardization guidelines, a systematic data management framework, and professional certification and training systems. The findings of this study are expected to serve as foundational references for improving scientific credibility and facilitating the introduction and development of an efficient construction forensic investigation system.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 국내건설 관련 사고에 대한 조사체계의 구조적 한계를 진단하고, 포렌식 기반 표준화 체계 구축의 필요성을 고찰하였다. 현행 조사체계는 발주기관·시공사·감리·행정기관 간 역할이 나누어져 있어 건설사고 원인 규명과 책임소재를 판단하는데 있어 객관성과 일관성을 확보하기에는 한계가 있다. 이러한 사고조사 구조는 중복 조사와 시간 지연 유발하고 분쟁을 장기화하여 사회-경제적 비용을 증가하게 된다. 본 연구는 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 기술적 증거 확보 절차와 사법적 절차를 통합한 기술과 법률의 융합형(Techno-Legal) 건설 포렌식 모델의 도입 필요성을 제안하였다. 아울러 국제표준인 ISO 기반의 표준화 지침과 데이터 관리체계 그리고 전문인력 인증과 양성체계 등 핵심 구성요소를 제시하여 건설사고 조사체계의 신뢰성과 효율성 제고 방안을 도출하였다. 본 연구결과는 건설사고에 대한 과학적 신뢰 확보와 효율적인 건설 포렌식 조사 시스템 도입과 개발의 기초자료로 활용될 것으로 기대된다.
-
Standardization Framework for Forensic Investigation of Construction Accidents
-
-
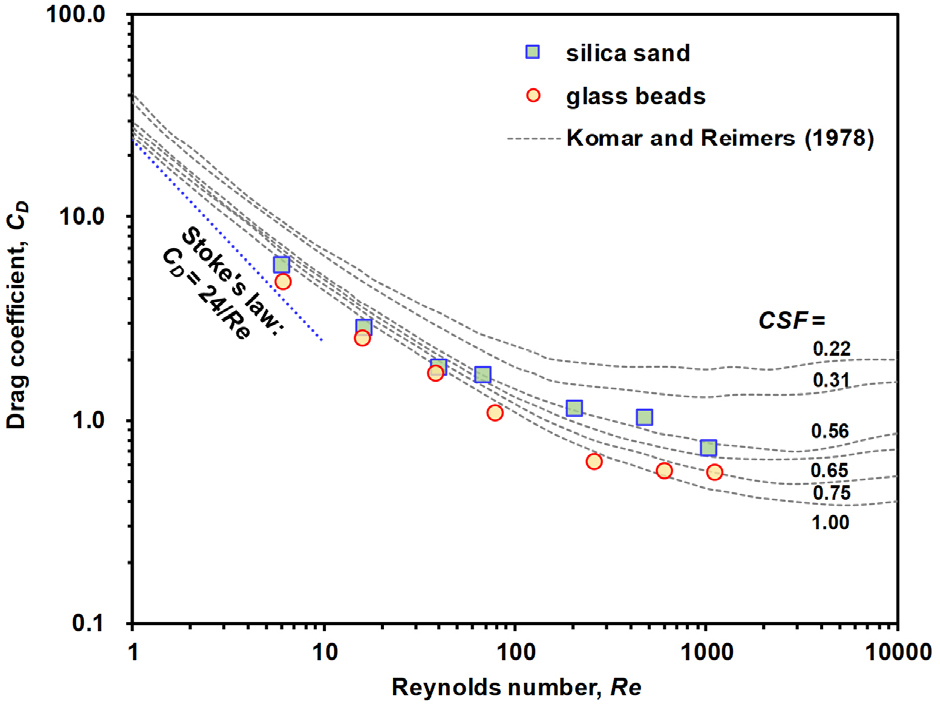
Influence of Particle Size Distribution on the Settling Velocity of Sand: An Effective Diameter-based Prediction Model
입도분포가 사질토의 침강속도에 미치는 영향 분석 및 유효 입경을 이용한 예측 모델 연구
-
Noeul Kim, Hyunwook Choo
김노을, 추현욱
- Accurate prediction of settling velocity is critical for evaluating the long-term stability of geotechnical structures and for consolidation design. However, conventional studies …
흙의 침강속도에 대한 정확한 예측은 지반 구조물의 장기 안정성 평가 및 압밀 설계에 필수적이다. 그러나 기존 연구들은 자연 퇴적물을 단일 입경으로 단순화하여 …
- Accurate prediction of settling velocity is critical for evaluating the long-term stability of geotechnical structures and for consolidation design. However, conventional studies have simplified natural sediments as uniform, single-sized particles, failing to account for the complex effects of particle size distribution (PSD). This study investigates the influence of PSD on settling behavior through laboratory experiments using silica sand and glass beads with a constant median particle size (D50) of approximately 0.7 mm but varying coefficients of uniformity (Cu). Settling velocities were measured using video tracking for single particles and a load-cell-based cumulative mass method for bulk-settling conditions. The results demonstrate that as the PSD widens, the drag coefficient (CD)–Reynolds number (Re) relationship deviates substantially from established guidelines, exhibiting a distinct settling lag. This behavior is attributed to excess pore water pressure generated by fine particles and to local upward flow induced by larger particles, which collectively hinder the descent of smaller particles. Quantitatively, D50-based predictions of the CD–Re relationship result in a high MAPE of over 130%. By introducing an effective particle diameter (Deff) based on the specific surface area, the MAPE is reduced to approximately 22%. Furthermore, a simplified correlation between Deff and Cu is proposed in this study, providing a practical and computationally efficient framework for predicting the settling velocity of nonuniform geomaterials.
- COLLAPSE
흙의 침강속도에 대한 정확한 예측은 지반 구조물의 장기 안정성 평가 및 압밀 설계에 필수적이다. 그러나 기존 연구들은 자연 퇴적물을 단일 입경으로 단순화하여 실제 퇴적물의 비균일한 입도분포 효과를 충분히 반영하지 못하는 한계가 있다. 본 연구는 이를 보완하기 위해 평균 입경(D50)을 0.7 mm로 고정하고 균등계수(Cu)를 변화시킨 silica sand와 glass beads를 대상으로 침강 실험을 수행하였다. 침강속도는 단일 입자의 경우 비디오 추적 기법을, 그룹 침강 조건에서는 로드셀 기반의 누적 질량 측정법을 통해 정밀하게 측정하였다. 실험 결과, 동일한 D50 조건에서도 입도분포가 넓어질수록 또는 시료가 비균일할수록 항력계수(CD)–레이놀즈 수(Re) 관계가 기존 가이드라인에서 크게 이탈하며 침강 속도가 지연되는 현상이 확인되었다. 이러한 현상은 미세 입자에 의한 과잉 간극수압 발현 및 조립 입자 침강 시 발생하는 국부적인 상승류가 미세 입자의 하강을 방해하는 수리학적 상호작용의 결과로 분석되었다. 정량적으로 D50을 대표 입경으로 사용할 경우 CD–Re 관계 예측오차(MAPE)가 130% 이상으로 매우 높게 나타났으나, 비표면적 기반의 유효입경(Deff)을 대표 입경으로 도입한 결과 오차율이 약 22% 수준으로 획기적으로 감소하였다. 최종적으로 본 연구에서는 Deff와 Cu 사이의 상관관계식을 제안함으로써, 비균일 퇴적물의 침강속도 산정에 대한 실무적 효율성과 예측 정확도를 동시에 향상시켰다.
-
Influence of Particle Size Distribution on the Settling Velocity of Sand: An Effective Diameter-based Prediction Model
-
-
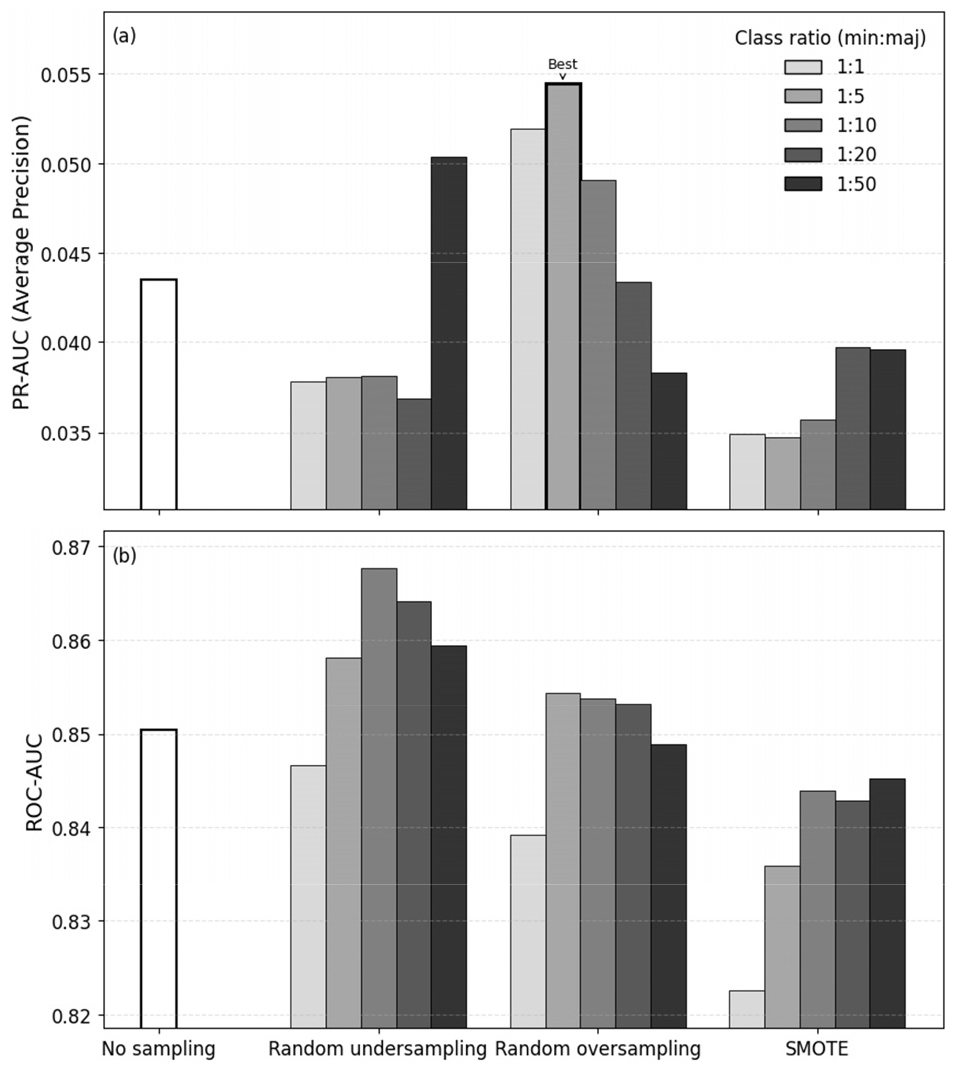
XGBoost-Based Prediction of Sewer-Induced Sinkholes Under Imbalanced Data Conditions
불균형 데이터 처리를 고려한 XGBoost 기반 하수관 손상 유발 지반함몰 예측 모델
-
Joonyoung Kim
김준영
- Prediction of ground subsidence caused by damaged sewer pipes is hindered by severe class imbalance due to the rarity of failure events. …
하수관 손상으로 인한 지반함몰 발생 예측은 발생 사례가 드문 특성으로 인해 극단적인 클래스 불균형 문제를 수반한다. 본 연구에서는 하수관 손상에 따른 지반함몰 …
- Prediction of ground subsidence caused by damaged sewer pipes is hindered by severe class imbalance due to the rarity of failure events. This study investigates the effect of imbalanced data handling strategies on machine-learning-based sinkhole prediction. An XGBoost classifier was adopted as the baseline model, and its performance without sampling was compared with that of models trained using random undersampling, random oversampling, and SMOTE under various class ratios. Model performance was primarily evaluated using PR-AUC, together with ROC-AUC, precision, recall, and F1-score. The results reveal that the baseline model achieved a relatively high ROC-AUC but relatively low PR-AUC, indicating limited capability in detecting rare sinkhole events. In contrast, random oversampling substantially improved minority-class prediction performance, with the highest PR-AUC observed at a class ratio of 1:5. These findings highlight the importance of PR-AUC-based evaluation and demonstrate that an appropriately designed oversampling strategy can effectively improve sinkhole prediction under highly imbalanced geotechnical data conditions.
- COLLAPSE
하수관 손상으로 인한 지반함몰 발생 예측은 발생 사례가 드문 특성으로 인해 극단적인 클래스 불균형 문제를 수반한다. 본 연구에서는 하수관 손상에 따른 지반함몰 발생 예측을 대상으로, 불균형 데이터 처리 기법이 기계학습 기반 예측 성능에 미치는 영향을 분석하였다. XGBoost 모델을 기본 분류기로 설정하고, 샘플링을 적용하지 않은 모델을 기준선으로 하여 random undersampling, random oversampling, SMOTE를 다양한 클래스 비율 조건에서 적용한 후 성능을 비교하였다. 성능 평가는 PR-AUC를 핵심 지표로 설정하고, ROC-AUC, 정밀도, 재현율, F1-score를 함께 고려하였다. 분석 결과, 기본 모델은 ROC-AUC 기준으로는 비교적 높은 값을 보였으나 PR-AUC는 상대적으로 낮아 소수 클래스 예측에 한계가 있음을 확인하였다. 반면, random oversampling을 적용한 모델은 소수 클래스 예측 성능이 유의미하게 향상되었으며, 특히 클래스 비율을 1:5로 설정한 경우 PR-AUC가 최대값을 나타냈다. 본 연구는 불균형 특성이 강한 지반함몰 예측 문제에서 PR-AUC 기반 평가의 중요성과 함께, 적절한 oversampling 전략의 효과를 실증적으로 제시한다.
-
XGBoost-Based Prediction of Sewer-Induced Sinkholes Under Imbalanced Data Conditions
-
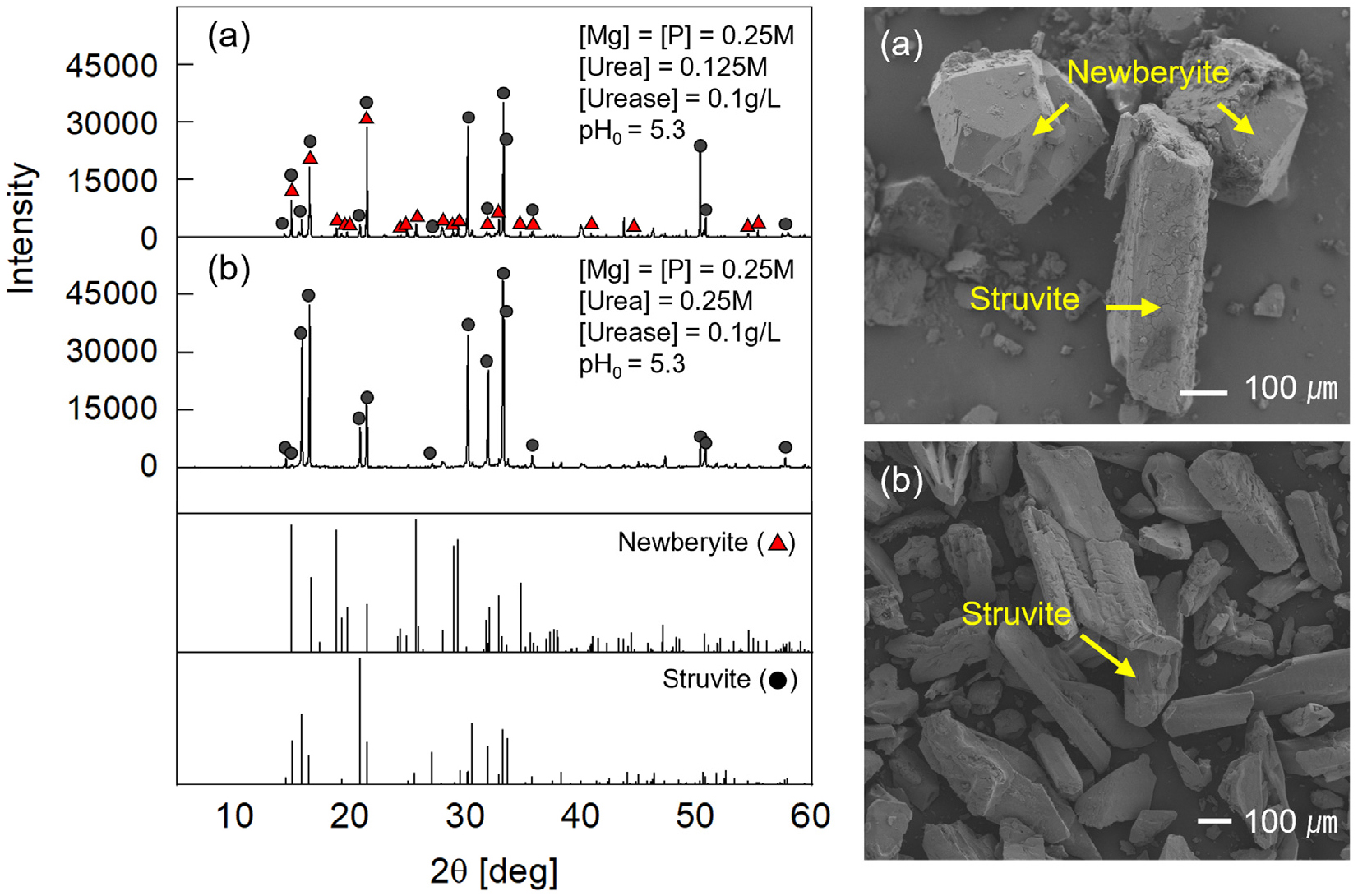
-
Evaluation of Enzyme-Induced Struvite Crystallization and Ground Improvement Feasibility
효소 유도 스트루바이트 결정화 과정 및 지반개량 적용 가능성 평가
-
Junghoon Kim, Daehyun Kim, Tae Sup Yun
김정훈, 김대현, 윤태섭
- Ammonium ions generated as byproducts of biocementation via urea hydrolysis may impact the environment. In this study, the process by which ammonium …
요소 가수분해 기반 바이오시멘테이션 공법은 탄산칼슘 침전을 통해 흙 입자 간 결합을 강화하고 공극을 채움으로써 지반의 강도 증진 및 투수성 저감 효과를 …
- Ammonium ions generated as byproducts of biocementation via urea hydrolysis may impact the environment. In this study, the process by which ammonium ions produced during free-urease-mediated urea hydrolysis are crystallized into struvite (MgNH4PO4·6H2O) was evaluated, and the feasibility for ground improvement was verified through laboratory experiments. A series of solution tests were conducted at a fixed urease concentration while the urea concentration and initial acidity were varied. The resulting amounts of struvite precipitation were then compared. The shear and bulk stiffness of sand specimens treated using the selected recipe were evaluated by monitoring shear and compressional wave velocities throughout the reaction period. In addition, the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) was measured. The results indicated that the maximum shear modulus increased approximately twofold after one day of reaction, whereas the bulk modulus decreased due to desaturation associated with CO2 gas generation. Furthermore, during the UCS tests, struvite precipitation induced the formation of aggregated soil clusters by binding sand particles, although the UCS could not be determined. This behavior suggests that the technique has potential for applications such as dust suppression.
- COLLAPSE
요소 가수분해 기반 바이오시멘테이션 공법은 탄산칼슘 침전을 통해 흙 입자 간 결합을 강화하고 공극을 채움으로써 지반의 강도 증진 및 투수성 저감 효과를 만들 수 있다. 하지만 반응 부산물로 생성된 암모늄 이온은 외부로 유출될 경우 부영양화 및 수질 저하 등 환경적 문제를 초래할 수 있어, 공법의 적용성 확대를 제한하는 요인으로 작용한다. 본 연구에서는 효소 기반 요소 가수분해 과정에서 발생하는 암모늄 이온을 스트루바이트(MgNH4PO4·6H2O)로 결정화하는 과정을 평가하고 이를 지반 내에 적용했을 때의 개량 가능성을 실내 실험을 통해 확인하였다. 먼저, 고정된 효소 농도 조건에서 요소 농도 및 초기 pH를 달리하며 일련의 용액 실험을 수행하였고, 용액 별 침전물 내 질소함량을 측정하여 스트루바이트 생성효율을 비교하였다. 다음으로, 선정된 혼합비 용액으로 처리한 시편의 강성도 및 강도는 탄성파(전단파 및 압축파) 속도 측정과 일축압축시험을 통해 평가하였다. 실험 결과, 스트루바이트 반응 1일 경과 후 최대 전단 탄성계수는 처리되지 않은 시료에 비해 약 2배 증가한 반면, 체적 탄성계수는 소폭 감소하였는데 이는 요소 가수분해 과정에서 발생한 CO2 기체가 시편의 포화도를 감소시켰기 때문으로 판단된다. 또한 일축압축시험에서 시편의 강도가 매우 작아 일축압축강도를 정량적으로 산정할 수 없었지만, 파괴 시 스트루바이트 침전에 의해 흙 입자들이 서로 결합하여 집합체를 형성하는 것이 관찰되었다. 이러한 결과는 본 기법이 표층처리 및 비산먼지 저감 분야에 적용될 수 있는 잠재성을 지니고 있음을 시사한다.
-
Evaluation of Enzyme-Induced Struvite Crystallization and Ground Improvement Feasibility
-

-
A Numerical Study on the Long-Term Temperature Distribution in Near-Field Rock for Underground Liquid Hydrogen Storage Systems
액화수소 지하저장시스템 근계 암반에서의 장기 온도분포 평가 수치해석 연구
-
Min-Jun Kim, Gyu-Hyun Go, Jong-Won Lee, Eui-Seob Park, Yong-Bok Jung, Myungsun Kim
김민준, 고규현, 이종원, 박의섭, 정용복, 김명선
- This study presents a preliminary numerical analysis of a conceptual model of an underground liquid hydrogen storage system to evaluate the long-term …
본 연구에서는 액화수소 지하저장시스템 개념모델을 대상으로 예비 수치해석을 수행하여 저장소 인근 암반의 장기 온도분포 및 ice ring 형성 특성을 평가하였다. 이를 위해 …
- This study presents a preliminary numerical analysis of a conceptual model of an underground liquid hydrogen storage system to evaluate the long-term temperature distribution in the near-field rock mass and the characteristics of ice-ring formation. A coupled thermal–hydraulic numerical model was developed, accounting for phase changes due to pore water freezing and the behavior of unfrozen water. The model was validated through freezing soil box experiments using porous media. The experimental and numerical results demonstrated similar formation patterns of the frozen wall, indicating that the developed model reasonably predicts the freezing behavior of porous media. Preliminary analysis using the validated model indicated that the temperature at the outermost boundary of the lining entered the subzero range approximately one year after storage, reaching –7°C after 50 years. The maximum ice-ring thickness was 2.5 m after 30 years and 5 m after 50 years. Design parameter analysis revealed that the ice-ring thickness after 50 years varied substantially, ranging from 3 to 15 m depending on the thermal conductivity of the insulation. Furthermore, a circular rock cavern shape tended to expand the freezing influence zone more than a horseshoe shape. The numerical model and preliminary findings of this study provide fundamental data for the conceptual design of underground liquid hydrogen storage systems and for sensitivity analysis of design parameters.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 액화수소 지하저장시스템 개념모델을 대상으로 예비 수치해석을 수행하여 저장소 인근 암반의 장기 온도분포 및 ice ring 형성 특성을 평가하였다. 이를 위해 공극수 동결에 따른 상변화와 부동수분 거동을 고려한 열–수리 완전 연계 해석 모델을 구축하고, 다공질 매질을 이용한 인공동결 토조 실험을 통해 모델을 검증하였다. 실험과 수치해석 결과에서 동결벽체의 형상 및 형성 패턴이 유사하게 나타나 구축된 모델이 다공질 매질의 동결 거동을 합리적으로 예측함을 확인하였다. 검증된 모델을 이용한 예비 해석 결과, 액화수소 저장 후 약 1년 경과 시 라이닝 최외곽 경계에서 영하 온도 영역에 진입하였고, 50년 경과 시 해당 경계 온도가 –7°C까지 저하되었다. 또한 ice ring의 최대 두께는 저장 후 30년 뒤 2.5 m, 50년 뒤에 5 m로 나타났다. 또한, 시스템의 일부 설계 인자 영향 분석을 수행하였으며, 절연체의 열전도도 변화에 따라 50년 후 ice ring 두께가 약 3–15 m 범위로 크게 달라졌다. 그리고 지하공동 형상에 따라 원형이 마제형보다 동결 영향 범위를 확대시키는 경향을 보였다. 본 연구의 수치해석 모델과 예비 해석 결과는 액화수소 지하저장시스템의 개념 설계 및 설계인자 민감도 평가를 위한 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
A Numerical Study on the Long-Term Temperature Distribution in Near-Field Rock for Underground Liquid Hydrogen Storage Systems
-
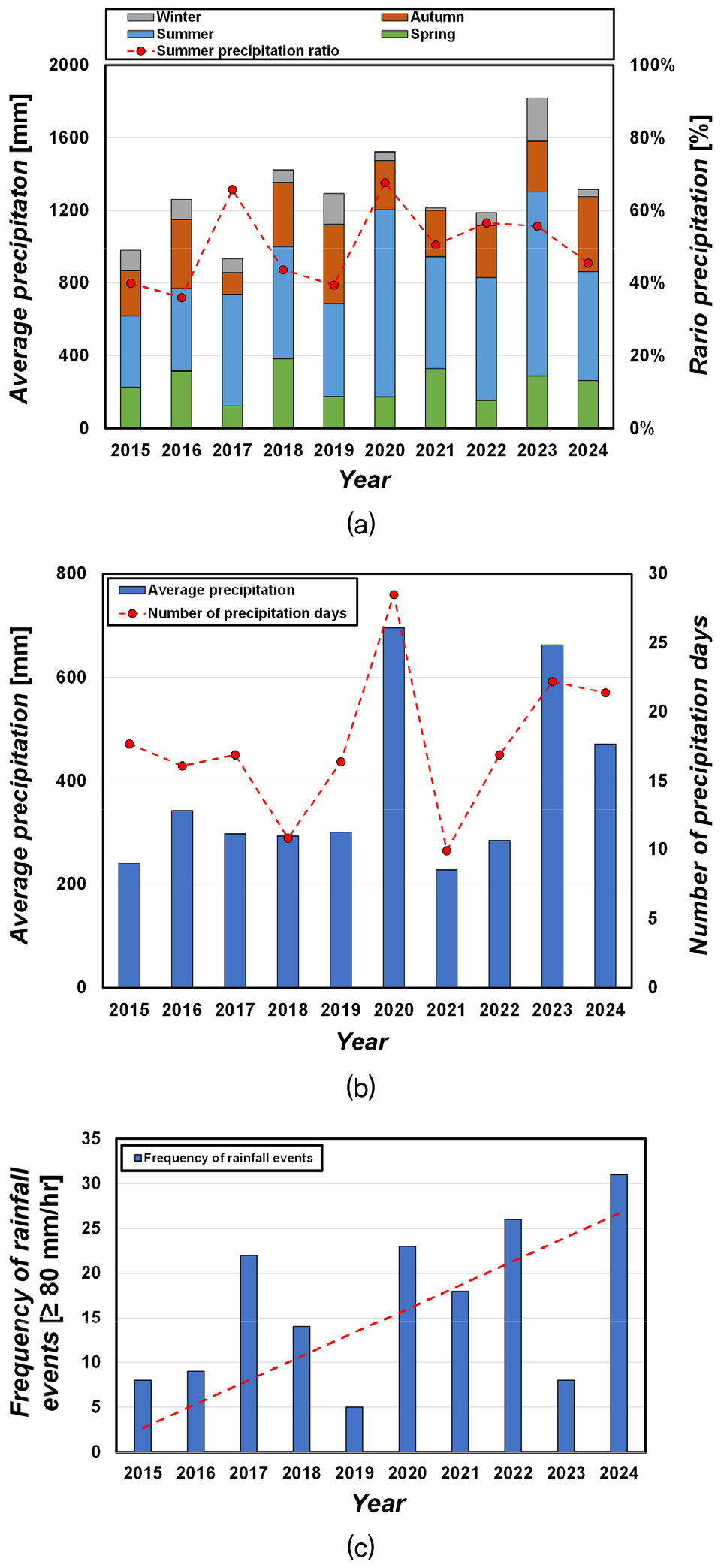
-
Disaster Risk Assessment Methods for Natural Steep Slopes Considering Rainfall and Social Impact Factors
강우와 사회적 영향 요인을 고려한 자연 급경사지 재해위험도 평가 방법의 개선 방안
-
Sojeong Kim, Jeongin Lee, Jinung Do
김소정, 이정인, 도진웅
- This study investigated the sensitivity of rainfall and social impact factors in steep slope disaster risk assessment using a weighted scoring method. …
본 연구는 자연 급경사지 재해위험도 평가에서 강우 요인과 사회적 영향 요인에 따른 민감도를 정량적으로 분석하고 가중치 적용 효과를 검토하였다. 분석 결과, 강우 …
- This study investigated the sensitivity of rainfall and social impact factors in steep slope disaster risk assessment using a weighted scoring method. Assigning weights to rainfall factors shifted the assessment toward higher risk grades, while social impact factors revealed greater susceptibility in residential and transportation areas than in park areas. When both factors were integrated, the proportion of high-risk grades (D and E) increased, improving the discriminatory capacity of the assessment and reducing grade concentration. These results demonstrate that weighted scoring enables more conservative and realistic risk estimation. Further refinement of weighting methods and the incorporation of climate-driven variables are recommended to improve the robustness of steep slope disaster risk assessment.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 자연 급경사지 재해위험도 평가에서 강우 요인과 사회적 영향 요인에 따른 민감도를 정량적으로 분석하고 가중치 적용 효과를 검토하였다. 분석 결과, 강우 요인에 가중치를 적용할 경우, 평가 결과가 상위 위험 등급으로 이동하면서 전반적인 재해위험도가 상승하였으며, 사회적 영향 요인을 반영한 경우, 공원시설에 비해 주거 및 교통 시설이 분포한 지역에서 인명 및 경제적 피해 취약성이 더 크게 나타났다. 강우 요인과 사회적 영향 요인을 복합적으로 고려했을 때 D‧E등급의 비율이 증가하여 재해위험도 평가의 변별력이 향상되고 등급 집중 현상이 완화되었으며, 이를 통해 보다 보수적이고 현실적인 재해위험도 산정이 가능함을 보여준다.
-
Disaster Risk Assessment Methods for Natural Steep Slopes Considering Rainfall and Social Impact Factors
-
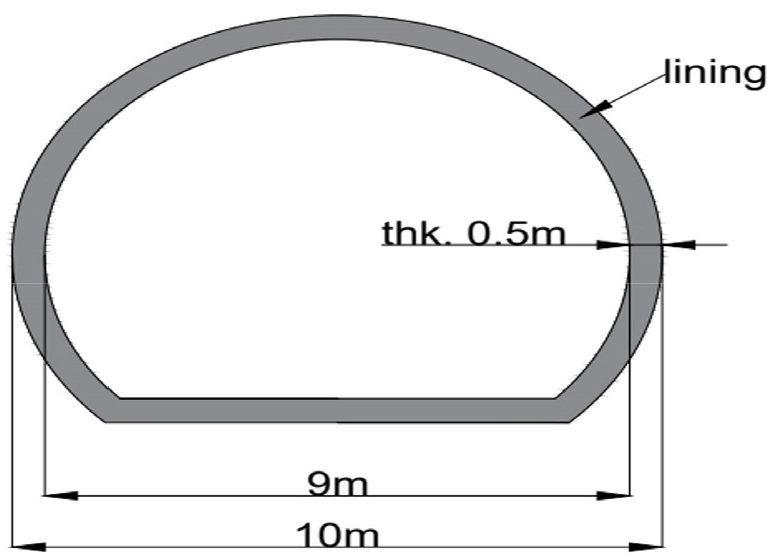
-
Dynamic Numerical Analysis and Behavior Assessment of Trenchless Tunnel Structures
비개착식 터널 구조물의 동적 수치해석 및 거동 분석
-
Dongha Baek, Byeong-Soo Yoo, Seokjung Kim, Mintaek Yoo
백동하, 유병수, 김석중, 유민택
- This study investigates the dynamic response characteristics of trenchless tunnels in rock masses, considering soil–structure interaction, and develops probabilistic seismic fragility functions. …
본 연구에서는 지반-구조물 상호작용(SSI)을 고려하여 암반 지반에 위치한 비개착식 터널의 동적 거동 특성을 분석하고, 확률론적 기법을 통해 지진 취약도 함수를 개발하였다. 이를 …
- This study investigates the dynamic response characteristics of trenchless tunnels in rock masses, considering soil–structure interaction, and develops probabilistic seismic fragility functions. Utilizing the nonlinear dynamic analysis program OpenSees, a two-dimensional numerical model was constructed to simulate the tunnel structure and surrounding rock. Geological conditions were classified into four cases based on rock stiffness: hard, soft, weathered, and fractured rock. A total of 120 ground motion scenarios were applied to evaluate the bending moment responses of the tunnel lining. The results demonstrate that the bending moments of the lining increase sharply as the rock stiffness decreases. Specifically, fractured rock (case 4) exhibits substantial seismic vulnerability, with structural responses exceeding the design flexural strength in 17 scenarios. The derived fragility functions indicate that tunnels in fractured zones have an approximately 35% probability of minor damage at a peak ground acceleration of 1.0 g. Accordingly, this study quantitatively evaluates the damage probability of vulnerable geological zones from a probabilistic perspective. The findings serve as a quantitative reference for establishing precise seismic designs and efficient reinforcement strategies for weak fractured rock zones.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 지반-구조물 상호작용(SSI)을 고려하여 암반 지반에 위치한 비개착식 터널의 동적 거동 특성을 분석하고, 확률론적 기법을 통해 지진 취약도 함수를 개발하였다. 이를 위해 비선형 동적 해석 프로그램인 OpenSees를 활용하여 터널 구조물과 암반을 모사한 2차원 수치 해석 모델을 구축하였다. 지반 조건은 암반 강성에 따라 경암, 연암, 풍화암 및 파쇄대의 4가지 케이스로 분류하였으며, 총 120개의 지진파 시나리오를 적용하여 터널 라이닝의 모멘트 응답을 산출하였다. 해석 결과, 라이닝에 발생하는 휨모멘트는 지반 강성이 낮아질수록 급격하게 증가하는 경향을 보였다. 특히 파쇄대 지반(Case 4)의 경우, 강지진 시 17개 지진파 시나리오에서 설계 휨강도를 초과하는 응답이 나타나 타 암반 지층 대비 높은 지진 취약성을 나타냈다. 이를 토대로 도출된 파쇄대 지반에 대한 지진 취약도 함수에 따르면, 파쇄대 구간의 터널은 PGA 1.0g 수준에서 경미한 손상 발생 확률이 약 35%에 이르는 것으로 분석되었다. 본 연구에서 제안한 지진 취약도 함수를 통해 파쇄대 지반의 손상 확률을 확률론적 관점에서 정량적으로 평가하였으며, 이는 상대적으로 연약한 파쇄대 구간에 대해 지반의 특성을 반영한 정밀한 내진 설계 및 보강 대책 수립을 위한 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Dynamic Numerical Analysis and Behavior Assessment of Trenchless Tunnel Structures
-
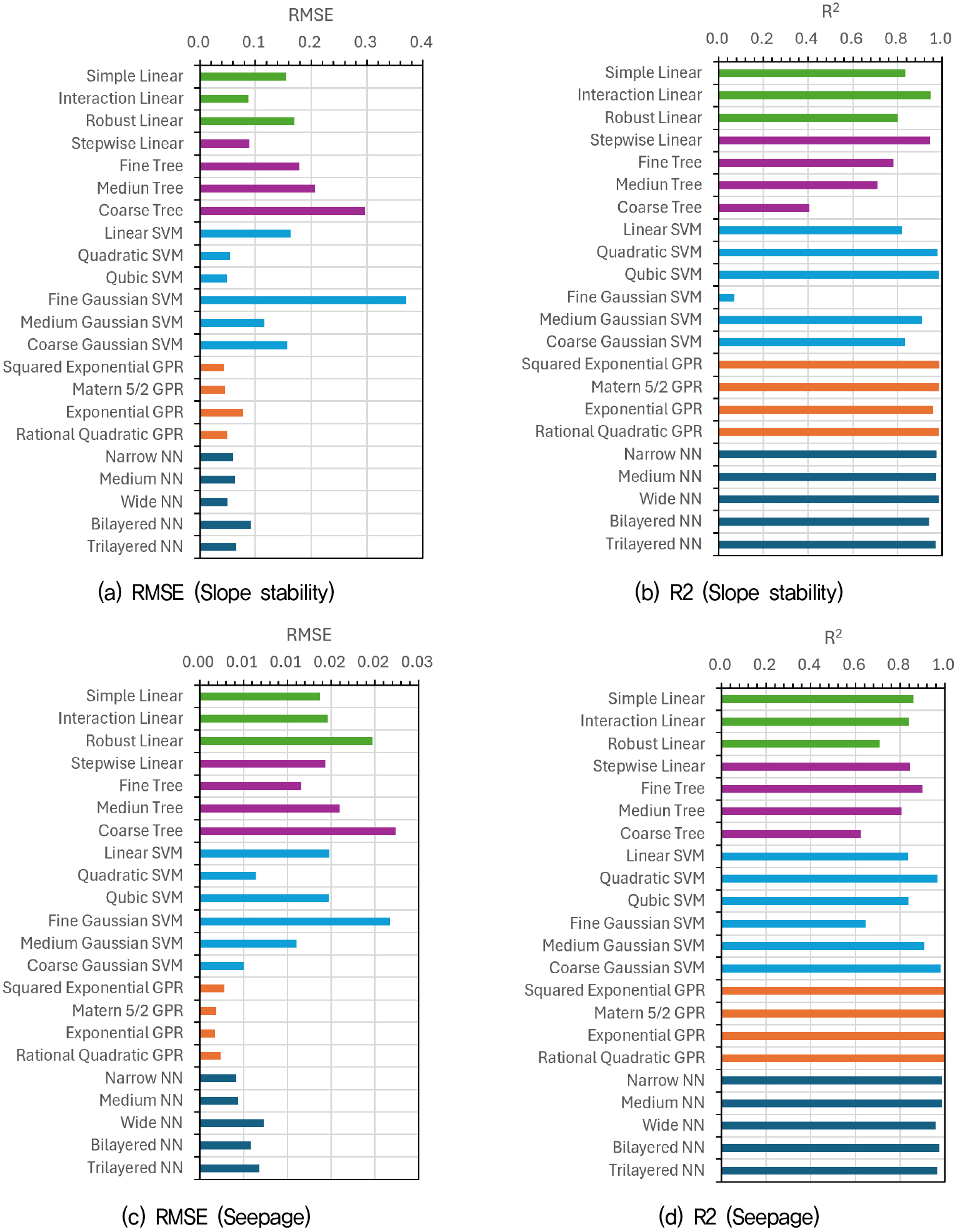
-
Probabilistic Stability Analysis of River Levees Using Machine-Learning-Based Surrogate Model
기계학습 기반의 대리 모델을 이용한 하천 제방의 확률론적 안정해석
-
Sung-Eun Cho
조성은
- Numerical analysis techniques have been widely used to evaluate the stability of river levees by capturing the complex hydraulic and mechanical behavior …
수치해석 기법은 지반의 복잡한 수리학적 및 역학적 거동을 분석하는 강력한 도구로 하천 제방의 안정해석에 널리 활용되고 있다. 그러나 하천 제방은 매우 작은 …
- Numerical analysis techniques have been widely used to evaluate the stability of river levees by capturing the complex hydraulic and mechanical behavior of geomaterials. However, river levees are designed to maintain extremely low failure probabilities; therefore, probabilistic analyses based on the direct application of Monte Carlo simulation (MCS) with repeated numerical analyses result in excessive computational costs. To address this limitation, this study applies machine learning techniques to the probabilistic stability analysis of river levees. Various machine learning models were trained using input–output data obtained from numerical analyses, and their predictive performance was evaluated using statistical metrics. A Gaussian process regression model, which exhibited the highest predictive accuracy, was selected as a surrogate model for MCS in probabilistic levee stability analysis. The results indicate that the application of a machine-learning-based surrogate model substantially improves computational efficiency compared to conventional probabilistic approaches based on numerical analysis, enabling stable and reliable evaluation of piping and slope failure probabilities and fragility curves.
- COLLAPSE
수치해석 기법은 지반의 복잡한 수리학적 및 역학적 거동을 분석하는 강력한 도구로 하천 제방의 안정해석에 널리 활용되고 있다. 그러나 하천 제방은 매우 작은 파괴확률 수준을 유지하도록 설계되므로 수치해석을 반복적으로 수행하는 직접적인 Monte Carlo Simulation(MCS)의 적용에 의한 확률론적 해석은 과다한 계산 비용을 유발한다. 이러한 단점을 극복하기 위하여 본 연구에서는 제방의 확률론적 안정해석에 기계학습을 적용하였다. 수치해석의 입력-출력 데이터를 기반으로 다양한 기계학습 모델의 학습을 수행하고 통계적 지표를 사용하여 학습된 모델의 예측성능을 평가하였다. 최종적으로 예측성능이 우수한 Gaussian Process Regression(GPR) 모델을 선정하여 제방의 확률론적 안정해석을 위한 MCS에 활용하였다. 연구 결과, 기계학습 기반의 대리 모델을 적용하면 기존 수치해석 기반의 확률론적 해석에 비해 계산 효율성의 큰 향상이 가능하여, 파이핑 및 사면 파괴 확률과 취약도 곡선을 안정적으로 평가할 수 있음을 확인하였다.
-
Probabilistic Stability Analysis of River Levees Using Machine-Learning-Based Surrogate Model
-

-
Evaluation of Soil Improvement Performance by Multiphase Mineralization Through Conversion of EICP Ammonium Byproducts to Struvite
EICP 암모늄 부산물의 스트루바이트 전환을 통한 복합 광물화 기반 지반개량 성능 평가
-
Junghoon Kim, Daehyun Kim, Tae Sup Yun
김정훈, 김대현, 윤태섭
- This study investigated the effectiveness of the multiphase mineralization of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and struvite (MgNH4PO4·6H …
바이오시멘테이션 공법은 탄산칼슘 침전을 통해 지반개량 효과를 제공할 수 있으나, 요소 가수분해 과정에서 발생하는 암모늄 이온은 해당 공법의 적용성을 제한하는 요인으로 작용한다. …
- This study investigated the effectiveness of the multiphase mineralization of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and struvite (MgNH4PO4·6H2O) from EICP byproducts for soil improvement. To precipitate both crystals into sand pores, an EICP solution formulation with pre-added magnesium ions was proposed. It was verified that the addition of magnesium ions did not affect CaCO3 precipitation or ammonium ion generation. After completion of the EICP reaction, the EICP solution containing magnesium and ammonium ions was mixed with an equal volume of phosphate solution over a range of pH values for struvite precipitation. As the pH of the phosphate solution increased, a larger fraction of ammonium ions was converted to struvite, while most of the previously precipitated CaCO3 was retained. To evaluate the affinity between CaCO3 and struvite crystals, glass slide experiments were conducted, and an unconfined compression test was performed to assess the effect of struvite precipitation on the strength of EICP-treated soils. The results indicated that struvite crystals did not adhere to CaCO3 surfaces, and the unconfined compressive strength increased by approximately 20% relative to that of specimens treated by EICP alone.
- COLLAPSE
바이오시멘테이션 공법은 탄산칼슘 침전을 통해 지반개량 효과를 제공할 수 있으나, 요소 가수분해 과정에서 발생하는 암모늄 이온은 해당 공법의 적용성을 제한하는 요인으로 작용한다. 이에 본 연구는 EICP로 탄산칼슘을 형성한 지반에서 암모늄 부산물을 스트루바이트(MgNH4PO4·6H2O)로 추가 침전시키는 복합 광물화 공정(즉, 탄산칼슘-스트루바이트 공존)을 제안하고, 그에 따른 지반개량 성능을 실험적으로 평가하였다. 탄산칼슘 생성 효율 및 암모늄 부산물의 스트루바이트 전환율을 최대로 하는 최적 공정을 결정하기 위해 본 연구에서는 EICP 용액에 마그네슘 이온을 선제적으로 투입하였으며, 용액 실험 결과 마그네슘 이온의 첨가는 탄산칼슘 침전 및 암모늄 이온 생성에 유의미한 영향을 미치지 않았다. EICP 반응 종료 후 마그네슘 이온 및 암모늄 이온을 포함한 EICP 용액과 서로 다른 pH 조건으로 조정한 인산염 용액을 1:1 부피비로 혼합하여 스트루바이트 침전을 유도하였다. 인산염 용액의 pH가 증가할수록 암모늄 이온의 스트루바이트 전환율이 증가하였으며 기존에 형성된 탄산칼슘은 대부분 유지되었다. 탄산칼슘과 스트루바이트 결정 간 접촉 특성을 평가하기 위해 유리 슬라이드 실험을 실시하였으며, 일축압축시험을 통해 스트루바이트 침전이 EICP 처리된 지반의 강도에 미치는 영향을 검토하였다. 시험 결과 스트루바이트 결정은 탄산칼슘 표면에 직접 부착되지 않는 양상을 보였으며 복합 광물화 시편의 일축압축강도는 EICP 단독 처리한 시료에 비해 약 20% 증가하였다. 이러한 결과는 EICP 암모늄 부산물의 스트루바이트 침전이 암모늄 이온 농도를 저감함과 더불어 EICP 처리 지반의 추가적인 강도 개선에 기여할 수 있음을 시사한다.
-
Evaluation of Soil Improvement Performance by Multiphase Mineralization Through Conversion of EICP Ammonium Byproducts to Struvite
-
-
Evaluation of the Black Ice Prevention Effect of PCM-Mixed Concrete Pavement Through Numerical Simulation
수치해석을 통한 상변화물질(PCM) 혼입 콘크리트 포장의 도로살얼음 예방 효과 분석
-
Jongki Lee, Gyu-Hyun Go
이종기, 고규현
- Black ice—a thin, transparent layer of ice that forms on road surfaces and reduces visibility—is a major cause of winter road accidents. …
도로살얼음은 도로 표면에 얇고 투명하게 형성되는 얼음층으로 시인성이 낮아 겨울철 대표적인 도로 안전사고의 원인으로 지목되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 도로살얼음 발생을 저감하기 위한 …
- Black ice—a thin, transparent layer of ice that forms on road surfaces and reduces visibility—is a major cause of winter road accidents. Through numerical analysis, this study evaluated the feasibility of using concrete infused with phase change materials (PCMs) as a road pavement material to reduce black ice formation. PCM-modified concrete specimens were fabricated, and temperature changes in PCM-modified concrete pavement under freezing conditions were measured. The thermal buffering effect was analyzed using the latent heat characteristics of the PCM-modified concrete specimens. Subsequently, a numerical model simulating the phase change behavior of PCMs was developed, and its predictive reliability was verified. Using the verified model, the temperature distribution and freezing area of concrete pavement were analyzed and compared for different PCM mixing ratios. The results indicated that PCM incorporation can substantially delay or reduce road ice formation. These findings suggest that the application of PCM-modified concrete is an effective alternative for reducing black ice formation on winter roads.
- COLLAPSE
도로살얼음은 도로 표면에 얇고 투명하게 형성되는 얼음층으로 시인성이 낮아 겨울철 대표적인 도로 안전사고의 원인으로 지목되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 도로살얼음 발생을 저감하기 위한 방안으로, PCM(상변화물질)이 혼입된 콘크리트의 도로 포장재 적용 가능성을 수치해석을 통해 평가하였다. PCM 콘크리트 공시체를 제작하고, 동결 조건에서 PCM 혼입 콘크리트 포장체의 온도 변화를 계측하여 PCM의 잠열 특성을 활용한 열적 완충 효과를 분석하였다. 이후 PCM의 상변화 거동이 반영된 수치해석 모델을 구축하고, 해당 모델의 예측 신뢰성을 검증하였다. 검증된 모델을 활용하여 PCM 혼입율에 따른 콘크리트 포장체의 온도 분포 및 동결 영역을 비교 분석하여 도로살얼음의 발생이 유의미하게 지연되거나 저감되는 효과를 확인하였다. 이러한 결과는 PCM 혼입 콘크리트의 적용이 겨울철 도로의 도로살얼음 발생을 저감하는 효과적인 대안이 될 수 있음을 시사한다.
-
Evaluation of the Black Ice Prevention Effect of PCM-Mixed Concrete Pavement Through Numerical Simulation
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society











